A 6-gene panel as a signature to predict recovery from advanced heart failure using transcriptomic analysis


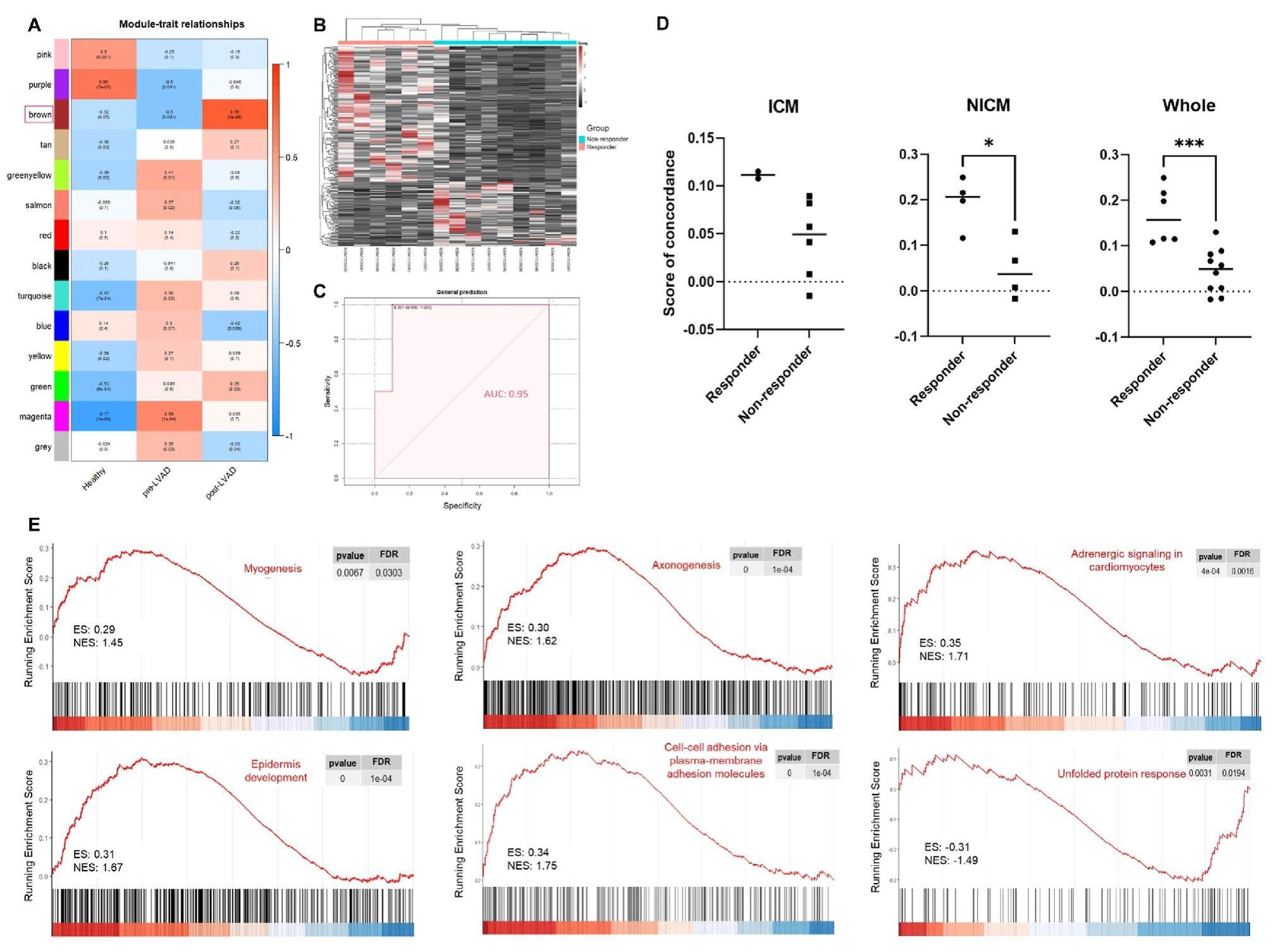
Heart failure (HF) is a global health problem with a high mortality rate. The various stimuli associated with HF can cause maladaptive remodeling, gradually weakening cardiac functions. Left ventricular assist device (LVAD) can improve advanced HF patients' cardiac functions, termed "reverse remodeling". However, only a small percentage of patients who have received LVAD have experienced reverse remodeling. Moreover, heart failure relapses in many patients after LVAD explantation, indicating that current biomarkers may not be sufficient to provide a complete view of pathological status. In this study, we identified a 6-gene panel (6GP; positive correlation: MYC, FOXO1, and ZFP36; negative correlation: LONRF1, FRZB, and NPPA), which demonstrated outstanding potential for predicting cardiac recovery, by combining weighted gene co-expressionanalysis (WGCNA) anddifferential gene expression analysis.6GP was highly correlated with key molecular signatures related to cardiac recovery, including myogenesis, axonogenesis, and epidermis development.