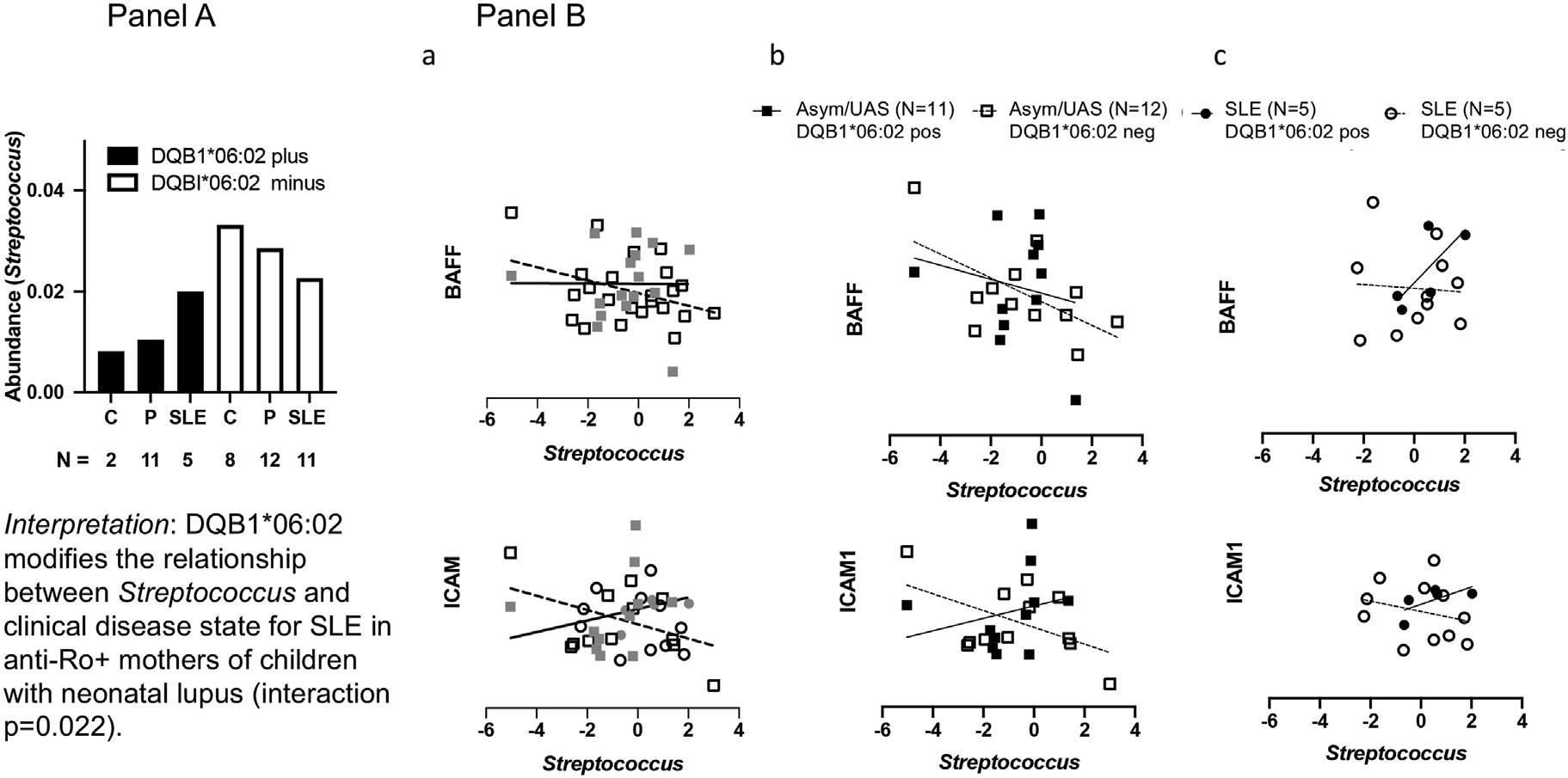
The modifying influence of HLA class II DQB1*06: 02 on the Streptococcus and clinical phenotype correlation among anti-RoD mothers of children with neonatal lupus


The genus Streptococcus, a gram-positive bacterium, contains species associated with immune activation at morbid outcomes, including scarlet fever, endocarditis, meningitis, and rheumatic fever. In both stool and saliva, there is a positive correlation between Streptococcus abundance and Sjogren's syndrome (SS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Interestingly, the HLA class II DQB1*06: 02 allele is both associated with the risk of SLE and plays putative roles in Streptococcus biology such as mimicry of bacterial antigens and related host antigens, an event that is associated with a loss of tolerance. We hypothesized that the Streptococcus-SLE association might be mediated by thep resence of SLE-risk allele DQB1*06: 02. Similarly, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), also known as CD54, and B-cell activating factor (BAFF), also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B (TNFSF13B), are elevated in the serum of SLE patients. The serum protein levels of BAFF and ICAM1 may therefore further complicate the interplay among Streptococcus sp., DQB1*06: 02, and SLE.