Targeting ferroptosis in cancer stem cells: A novel strategy to improve cancer treatment
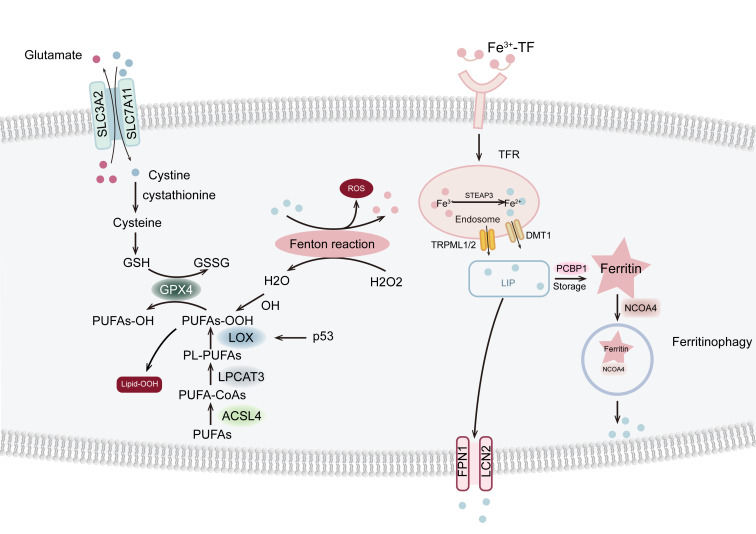
Ferroptosis, a distinct regulated cell death process characterized by iron retention and lipid peroxidation, plays a crucial role in the survival of cancer stem cells (CSCs), key contributors to cancer initiation, progression, and recurrence. CSCs exhibit enhanced iron uptake and altered lipid metabolism, allowing them to evade conventional therapies and persist within the cancer microenvironment. Their resilience is linked to low reactive oxygen species levels, aiding survival under oxidative stress. Key regulatory pathways, including the cystine/glutathione axis, significantly modulate CSCs' sensitivity to ferroptosis by maintaining a balance between antioxidant defenses and pro-oxidative stressors. Targeting ferroptosis in CSCs offers promising therapeutic avenues for enhancing treatment efficacy and overcoming resistance. Strategies such as pharmacological inhibition of the SLC7A11 transporter, which reduces cysteine availability and glutathione levels, can potentiate ferroptosis in CSCs. Additionally, inducing dysregulation of iron metabolism or lipid peroxidation can selectively compromise CSCs' survival. Nanoparticle drug delivery systems that increase intracellular iron and reactive oxygen species levels are proving effective in targeting CSCs with minimal impact on normal cells. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between ferroptosis and CSCs' biology is essential for developing innovative strategies aimed at eradicating these elusive cells, thereby improving cancer treatment outcomes and reducing recurrence rates.
Endothelial cell in tumor angiogenesis: Origins, mechanisms, and therapeutic implication
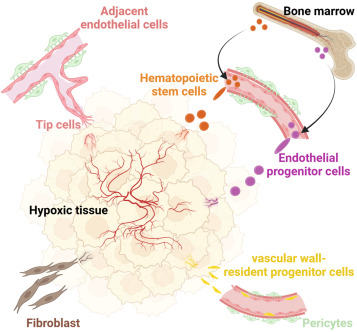
A hallmark feature of cancer is its capacity to induce the development of new blood vessels. Anti-angiogenic therapies are commonly employed to combat various types of cancer. Despite notable advancements in this field, limited efficacy and resistance remain critical challenges. While anti-angiogenic therapy primarily targets endothelial cells within the abnormal vasculature, the origins of tumor vascular endothelial cells in solid tumors remain a subject of ongoing debate. Unraveling the origins of these endothelial cells is crucial for developing more effective strategies to combat tumor angiogenesis. This review summarizes the latest findings on the origins of endothelial cells in tumor angiogenesis and explores the progress, limitations, and future directions of anti-angiogenic therapy.