Systematic analysis of clinical relevance and molecular characterization of m6A in COVID-19 patients


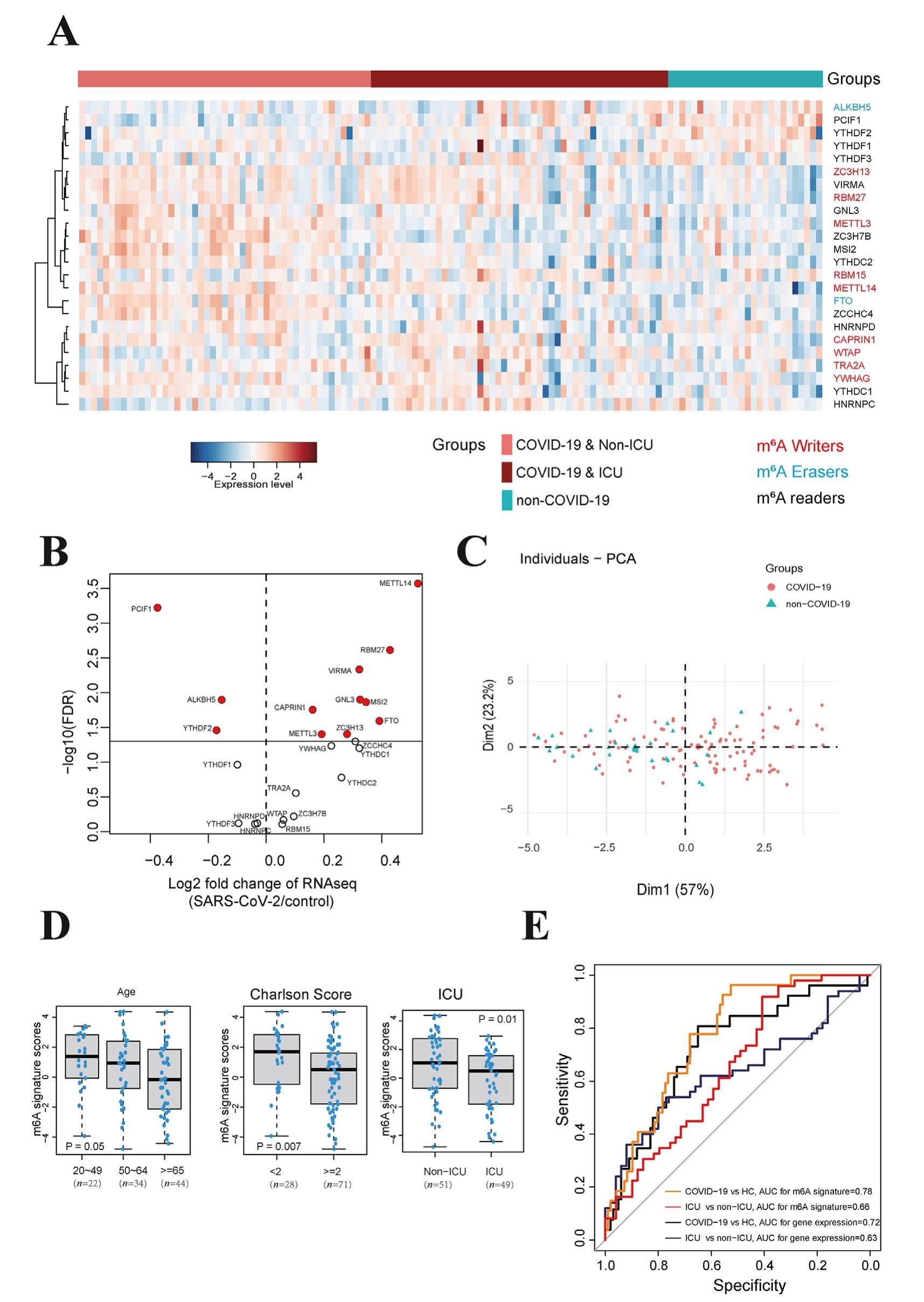
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent posttranscriptional RNA modification in mRNA and long noncoding RNAs of eukaryotes, and its biological functions are mediated by m6A writers, erasers and readers. A nuclear methyltransferase complex consisting of METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, VIRMA, ZC3H13, RBM15 (or RBM15B), YWHAG, TRA2A and CAPRIN1 catalyzes the m6A modifications, acting as m6A writers. m6A demethylase ALKBH5 as well as m6A demethylase FTO mediate the demethylation of m6As, acting as the m6A erasers. A variety of proteins including YTH domain-containing proteins can bind m6A marks as the m6A readers. The role of mRNA m6A methylation in COVID-19 patients is of great concern due to reports that m6A may provide potential new strategies for the development of vaccine and antiviral drug. For instance, Jun'e et al reported that m6A regulators regulate m6A during SARS-CoV-2 infection in Huh7 cells. Other studies also show that m6A regulators METTL3 and RBM15 are able to regulate host cell innate immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection in Caco-2 cells and HuT 78 cells, respectively. Hannah et al found that METTL3 affects SARS-CoV-2 replication in A549 cells, and they found that targeting the m6A RNA modification pathway can block SARS-CoV-2 replication. Although many studies have focused on the function and molecular mechanism of m6A in cell lines infected with SARS-CoV-2, the clinical relevance and basic molecular characterization of m6A in vivo have been neglected, which deserves further exploration.