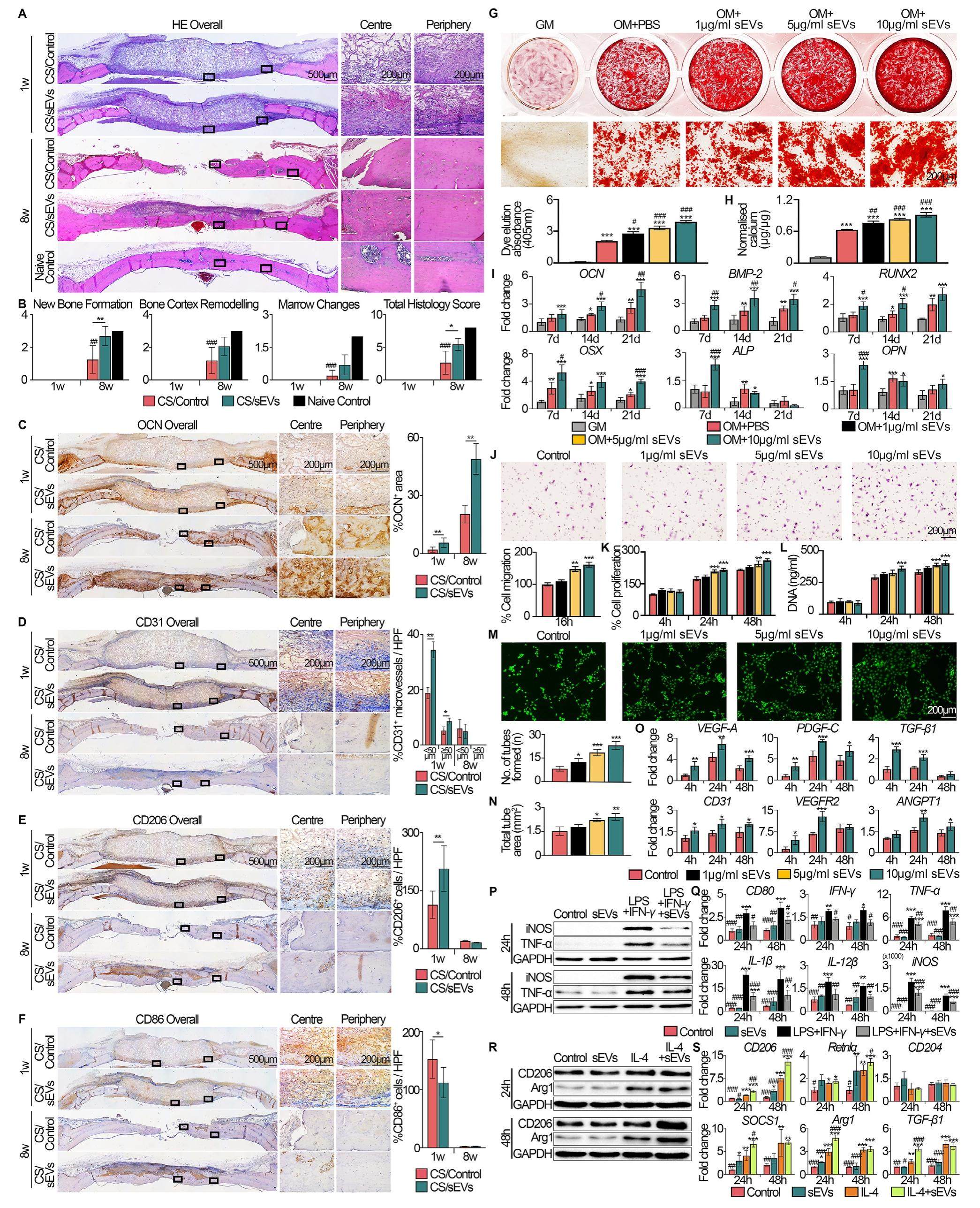
Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived small extracellular vesicles modulate macrophage polarization and enhance angio-osteogenesis to promote bone healing


Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) have demonstrated therapeutic efficacy for bone regeneration in animal and clinical studies. Although MSCs were initially thought to differentiate to various cell types to replace the injured/diseased tissue, it is now accepted that these cells secrete factors to promote tissue repair. Among these factors, small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) of size 50-200 nm, which include the exosomes, have been identified as the principal agent mediating the wide-ranging therapeutic efficacy of MSCs. Several studies have also reported the therapeutic effects of MSC-sEVs to enhance bone repair in animal models, as recently reviewed. However, the cellular processes and mechanisms mediated by MSC-sEVs in bone regeneration remain to be fully elucidated.