LncRNA MIR205HG expression predicts efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with locally advanced breast cancer


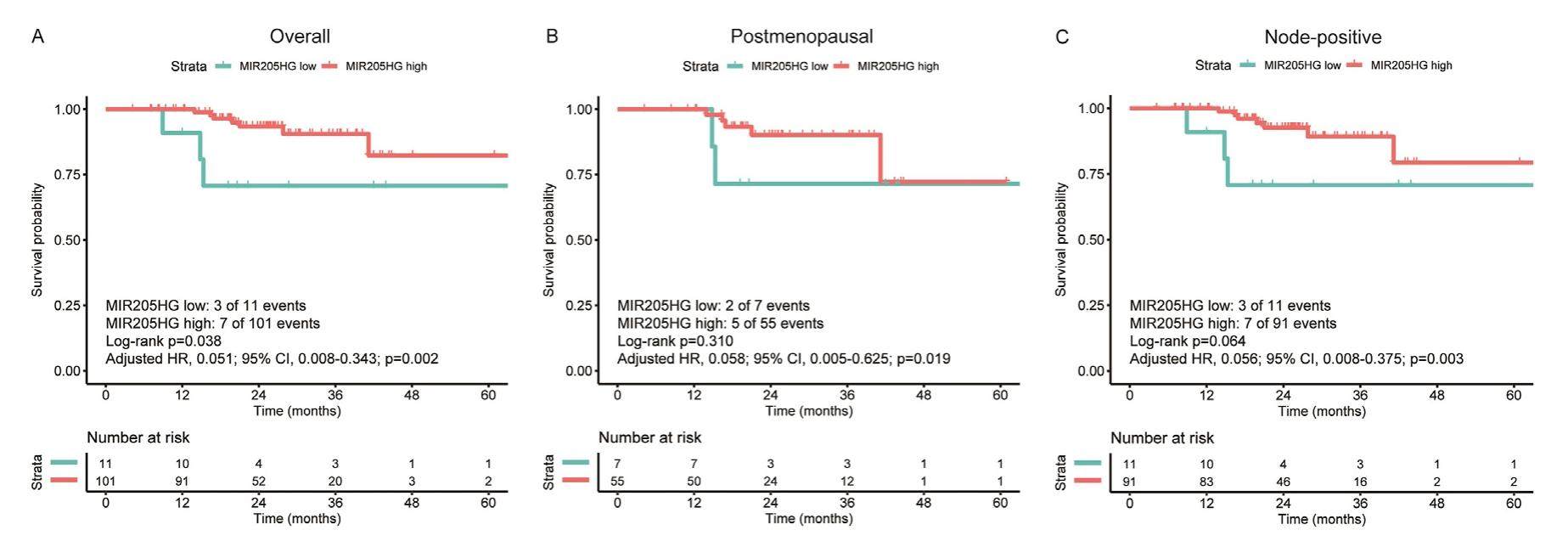
Recent studies reported that lncRNA MIR205HG expression is associated with sensitivity to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) drug in lung cancer cells. However, few clinical studies reported the role of this molecule in breast cancer, particularly in the neoadjuvant setting. In thisstudy, we explored the clinical significance of MIR205HG expression with its predictive and prognostic value for patients with locally advanced breast cancer. It turned out that MIR205HG is a downregulated lncRNA in breast cancer compared with adjacent nontumor tissues. While it's positively associated with estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR), it's reversely related to human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and Ki67 index. Importantly, MIR205HG expression level could serve as an independent predictive factor of pathological complete response (pCR) and an independent prognostic factor of relapse-free survival (RFS) for the neoadjuvant cohort. Analysis of public databases suggested that MIR205HG expression is associated with better survival outcomes. Furthermore, pathway analyses revealed the potential function of MIR205HG in transcriptional misregulation in cancer. Therefore, MIR205HG might be a promising novel biomarker of pCR and survival outcomes for patients with locally advanced breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy.