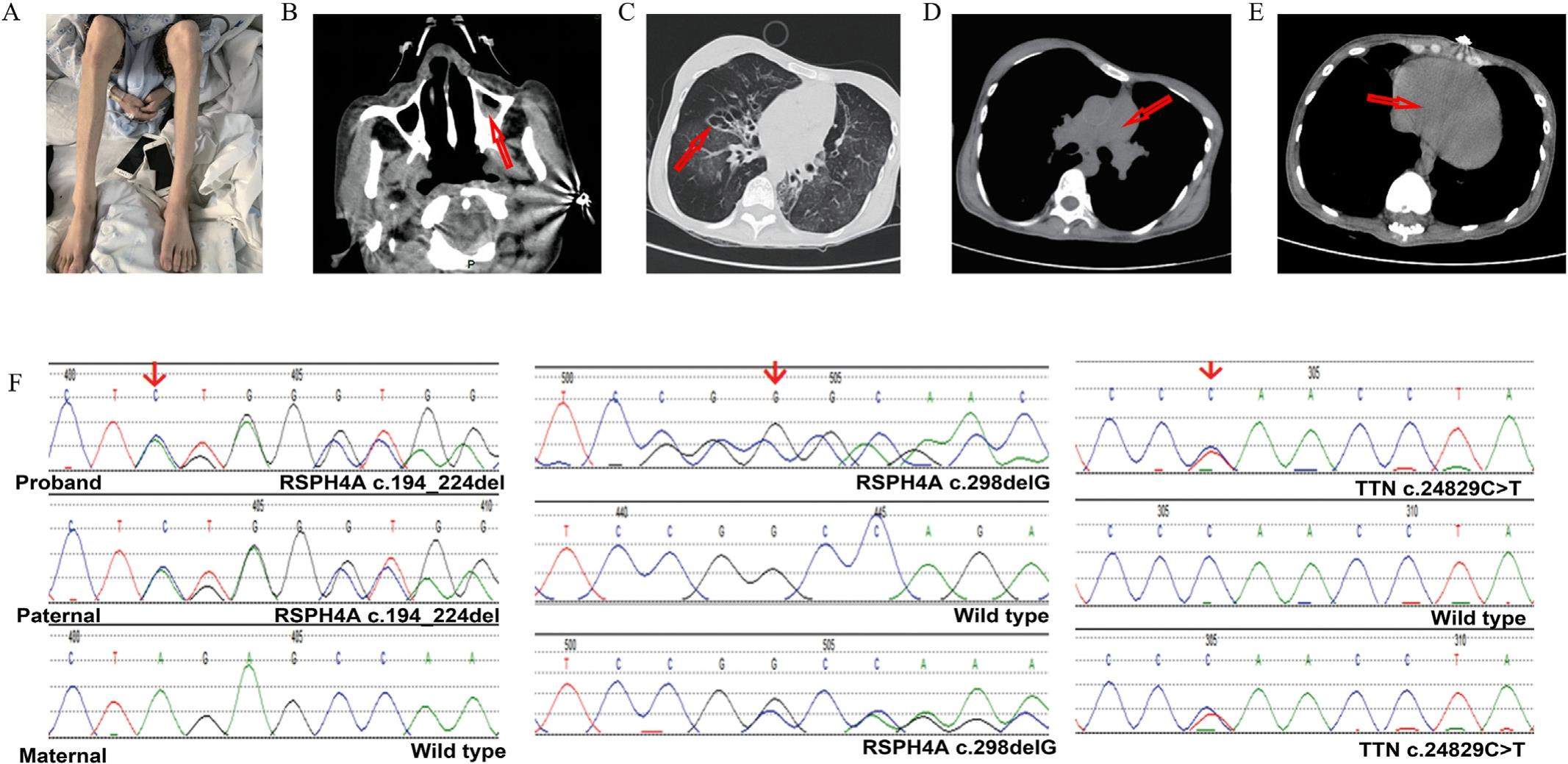
Novel mutations in RSPH4A and TTN genes lead to primary ciliary dyskinesia-hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure overlap syndrome


Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) is an autosomal recessive disease caused by defects in motile cilia and clinically characterized by bronchiectasis, situs inversus, nasosinusitis, recurrent respiratory infections, tympanitis, and/or male infertility. In PCD, impaired function or structure of motile cilia leads to abnormality of mucociliary clearance, and RSPH4A (encoding radial spoke head protein) mutation has been recognized as a major causative factor. Hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure (HMERF) is an autosomal dominant myopathy due to mutations in TTN gene (encoding the fibronectin III domain of titin). HMERF is an extremely rare condition characterized by severe respiratory involvement at onset and muscle weakness starting in the third to fifth decades of life.