Acute liver injury induces expression of FGF23 in hepatocytes via orphan nuclear receptor ERRγ signaling


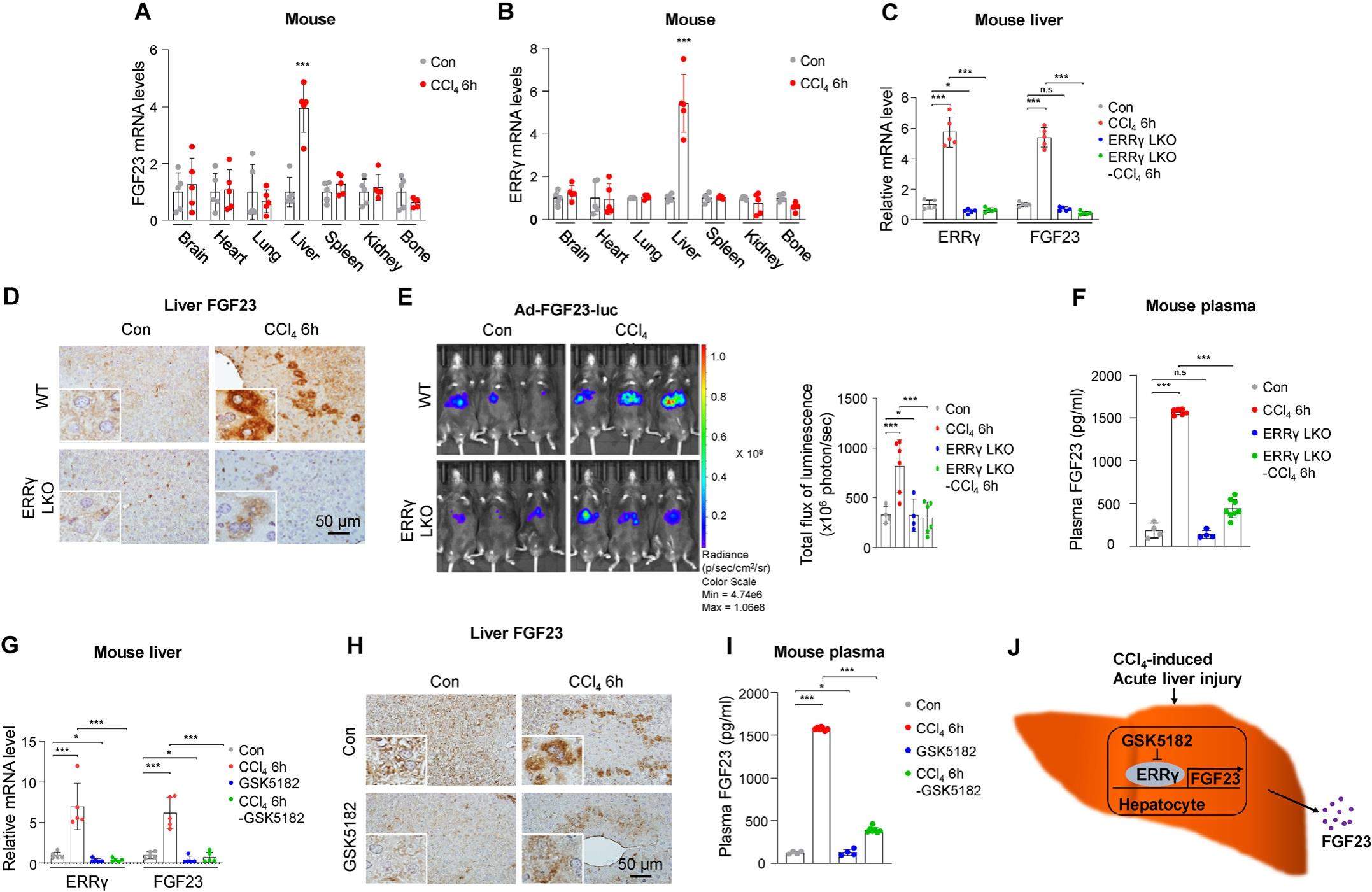
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is an osteocyte-and osteoblast-derived hormone that primarily regulates phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. Circulatory FGF23 levels are abnormally increased in pathological conditions like acute or chronic kidney injury, resulting in disease progression as well as increased rates of morbidity and mortality. However, FGF23 production in acute liver injury is not fully investigated. In this study, we report that carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) -induced acute liver injury upregulates hepaticestrogen-relatedreceptorgamma (ERRγ) and FGF23 gene expression and FGF23 secretion from liver. Hepatocyte specific depletion of ERRγ bluntedCCl4-induced hepatic FGF23 promoter activity, FGF23 gene expression and FGF23 levels. Further, treatment with ERRγ-specific inverse agonist GSK5182 also efficiently inhibited CCl4-induced acute liver injury-mediated hepatic FGF23 gene expression and circulatory FGF23 levels in vivo. Taken together, these results firstly describe a detailed molecular mechanism of hepatic FGF23 gene expression induction in an acute liver injury condition. Further, we present evidence that inhibiting ERRγ transactivation by the small molecule GSK5182 may be a useful strategy to control the devastating circulatory levels of FGF23.