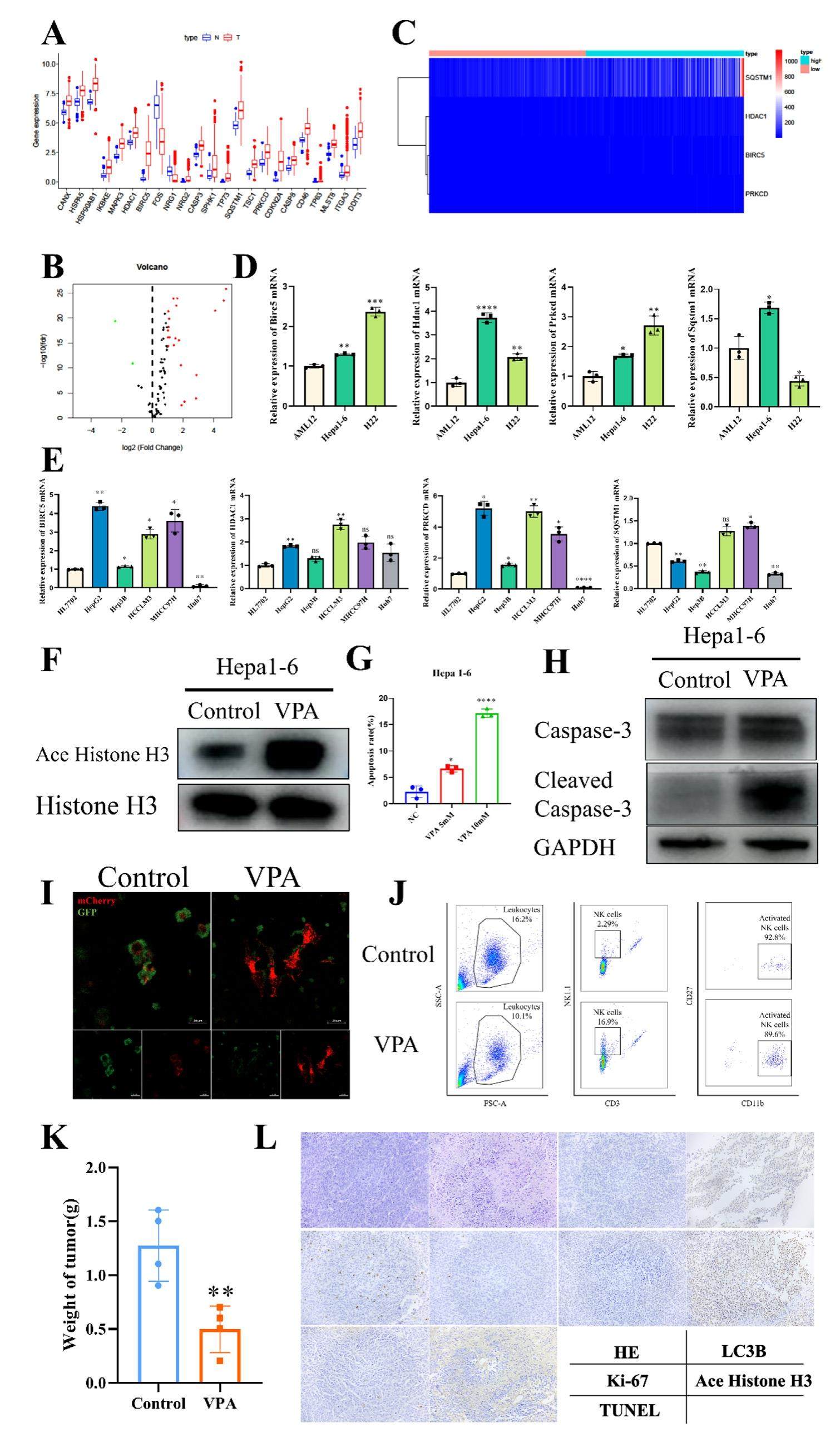
ARIG inhibition improves the prognosis of liver cancer through autophagy regulation and tumor immunity enhancement


Currently, the primary treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a comprehensive treatment based on surgery. In the case of advanced HCC that may not be removed surgically, additional issues, such as drug resistance and drug inefficacy with long-term use of chemotherapeutic drugs, highlight the pressing need for new treatment strategies. Autophagy plays an essential role in cellular physiology, which was reported to modulate components of the immune system. Autophagy-related immune genes (ARIGs) are linked to both autophagy and immunity. Here we identified histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), an ARIG strongly expressed in HCC, as a therapeutic target. Then valproic acid (VPA), a specific inhibitor of HDAC1, was used to treat liver cancer in vitro and in vivo. The results demonstrated that VPA could significantly induce autophagy and apoptosis of Hepa1-6 cells and inhibit tumor growth in vivo. This effect could be related to the regulation of autophagy and tumor immune microenvironment by VPA.