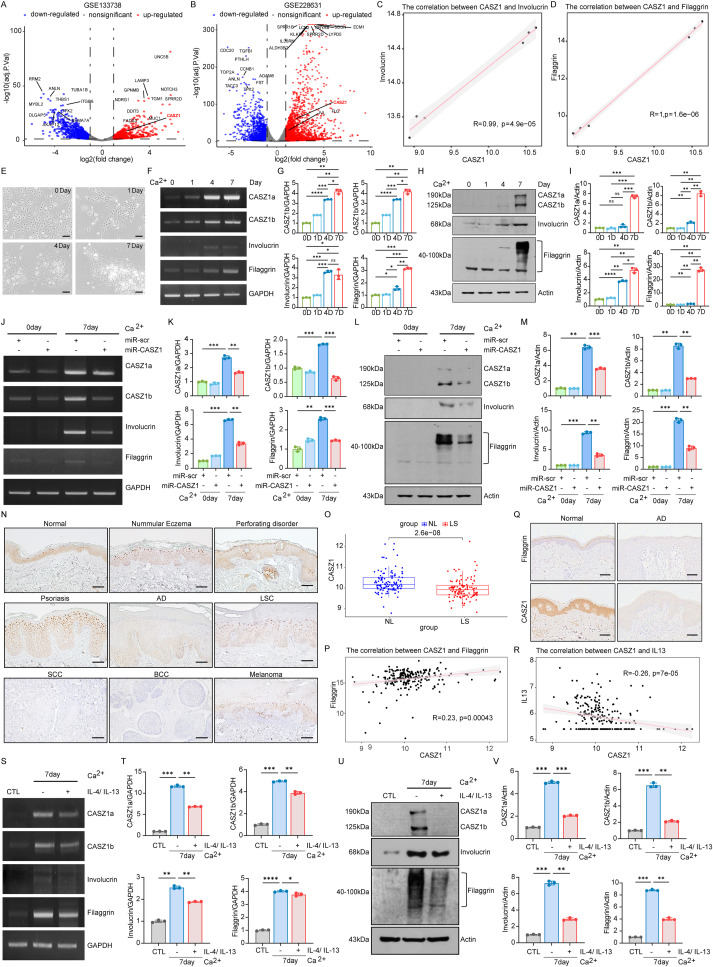
The regulatory role of CASZ1 in keratinocyte differentiation and skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis


The skin, being the largest organ of the human body, serves a critical barrier function by preventing the intrusion of harmful external substances and minimizing moisture loss. The epidermis consists of a stratified epithelium of continuously differentiating keratinocytes (KCs), which originate from the basal layer and progressively migrate upwards to form the stratum corneum. Proper epidermal differentiation is essential for maintaining the skin’s barrier function.1 However, disruptions in this process can lead to various skin diseases, including psoriasis, atopic dermatitis (AD), and squamous cell carcinoma.2 Thus, elucidating the regulatory network that governs epidermal differentiation is crucial for understanding the pathogenesis of these skin diseases.