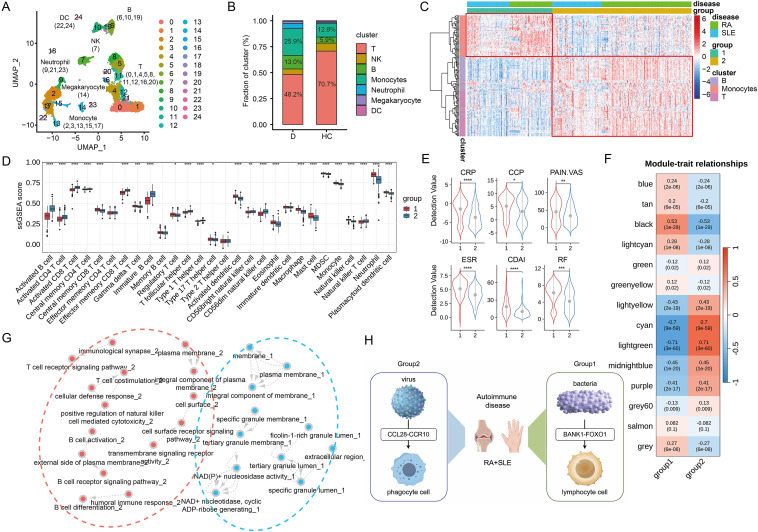
Identifying functional subtypes and common mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus


There are similarities between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in terms of clinical manifestations, immune responses, and therapeutic strategies,1 and thus a joint analysis of the two diseases could contribute to a deeper understanding of the shared pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. The subtype analysis of RA and SLE is currently understudied, and the marker genes used for subtype definition in most studies are derived from bulk RNA sequencing data or microarray data, which are underrepresentative of individual immune cell status.2 Therefore, we aimed to identify cell type-specific expressed genes as biomarkers based on single-cell RNA sequencing data and to explore the commonalities and differences between RA and SLE by a combined subtype analysis based on microarray data. Both the representativeness of the markers in terms of immune characteristics and the reproducibility of the results are ensured by the sufficient sample size. Immune infiltration analysis revealed the subtype heterogeneity and significant differences in clinical characteristics between different subtypes of RA patients, which verified the heterogeneity between different subtypes. Finally, we constructed subtype prediction models by machine learning algorithms further validating the heterogeneity among subtypes. Detailed methodology and the overall flowchart (Fig. S1) are provided in the supplementary material.