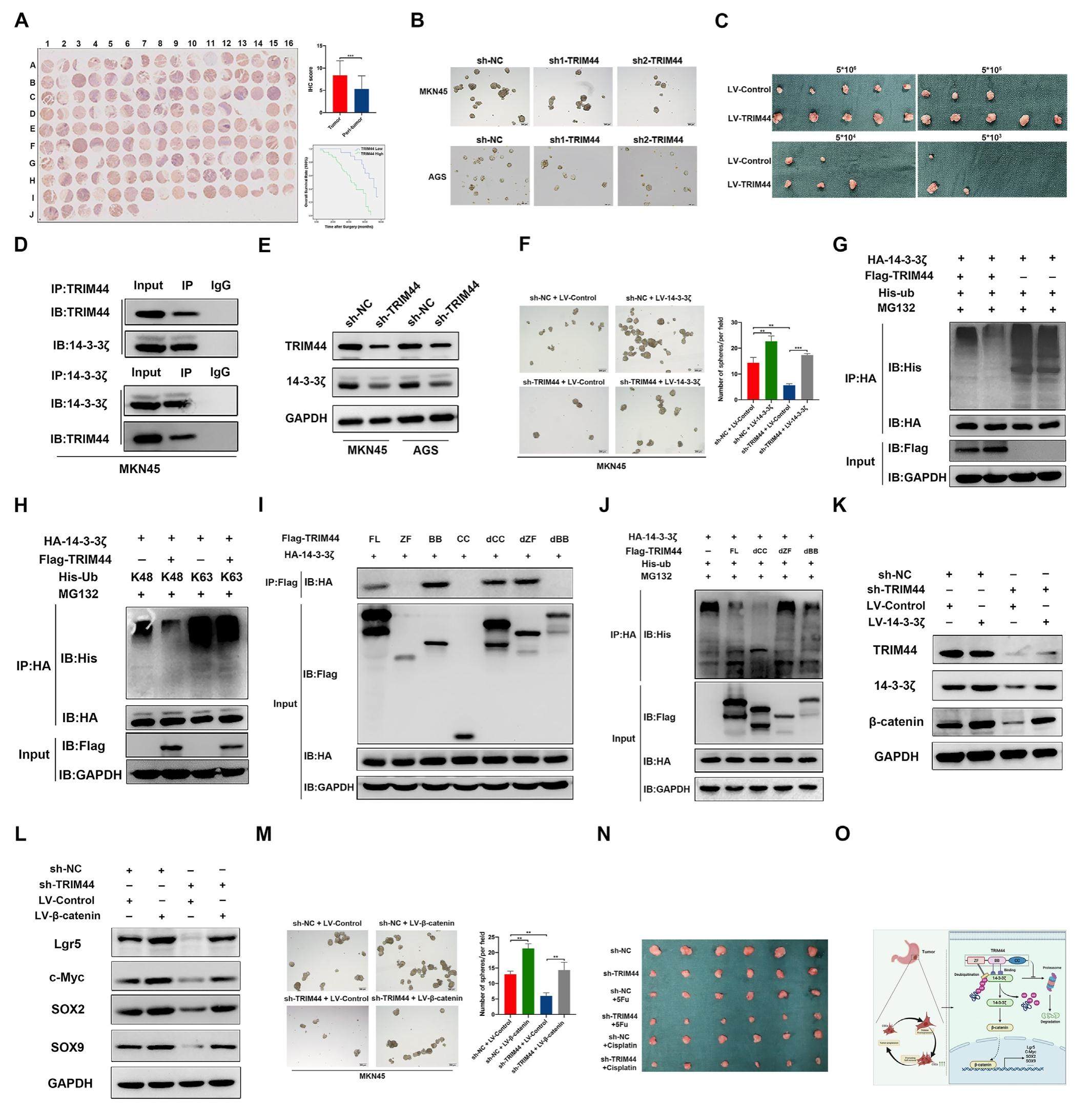
Elevation of TRIM44 potentiates propagation of gastric cancer stem cells


Gastric cancer stem cells (CSCs), which refer to treatmentrefractory and self-renewal cell populations, are critically involved in the initiation and progression of gastric cancer (GC). Although gastric CSCs populations have been validated across multiple studies, the precise molecular mechanisms of gastric CSCs properties maintenance remain unclear. Emerging evidences have highlighted the role of tripartite-motif (TRIM) family members in regulating CSCs self-renewal and differentiation through protein ubiquitination modification. However, the effects of TRIM family members on GC and gastric CSCs have not been elucidated. In this study, we identified TRIM44 (one of the TRIM family members) is overexpressed in human GC and gastric CSCs, and associates with GC progression and poor prognosis. In addition, our findings revealed a crucial role of TRIM44/14-3-3z/b-catenin signaling in inducing gastric CSCs properties, thus supporting their function as potential therapeutic targets in modulating GC proliferation and chemoresistance.