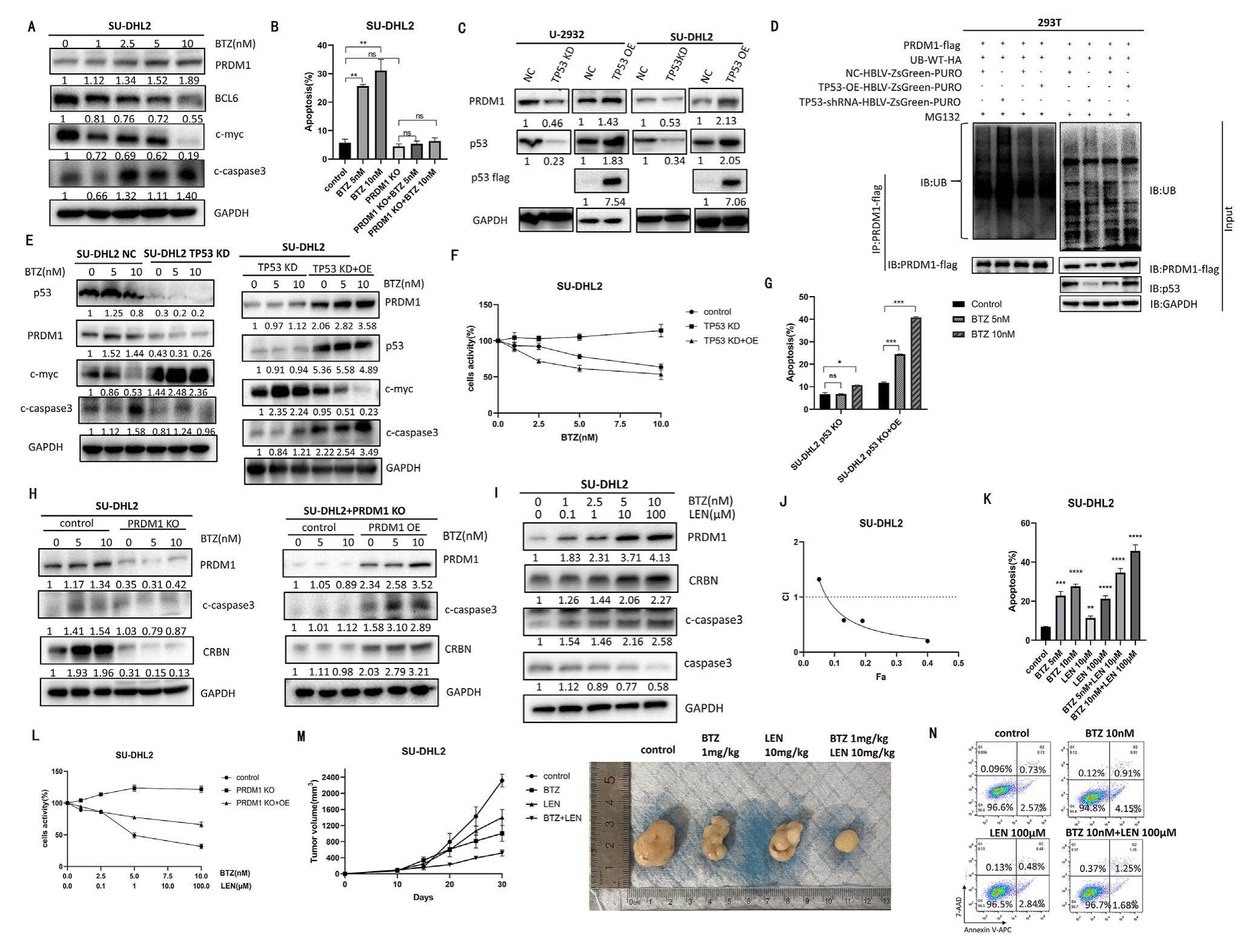
Bortezomib depended on PRDM1 and TP53 to exert therapeutic effect in activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma


PR/SET domain 1 (PRDM1) gene is located on chromosome 6q21, encoding the B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1 (BLIMP1). It is reported that loss of PRDM1 function is exacerbated in activated B-cell-like (ABC) -diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and associated with inferior survival. However, it remains unclear what leads to PRDM1 inactivation and the drug resistance mechanism caused by abnormal inactivation of PRDM1. We investigated the contribution of PRDM1 gene as a prognosis and potential therapeutic target for ABC-DLBCL patients and further clarified the possible mechanism of PRDM1 abnormal inactivation. We first proposed that TP53 could regulate PRDM1 by histone ubiquitination modification at the post-transcriptional level. Moreover, the therapeutic effect of bortezomib was dependent on PRDM1 and TP53, and a synergistic effect of lenalidomide and bortezomib was observed in PRDM1-mutated ABC DLBCL cell lines, which provided a theoretical reference for overcoming drug resistance in PRDM1-mutated ABC-DLBCL patients.