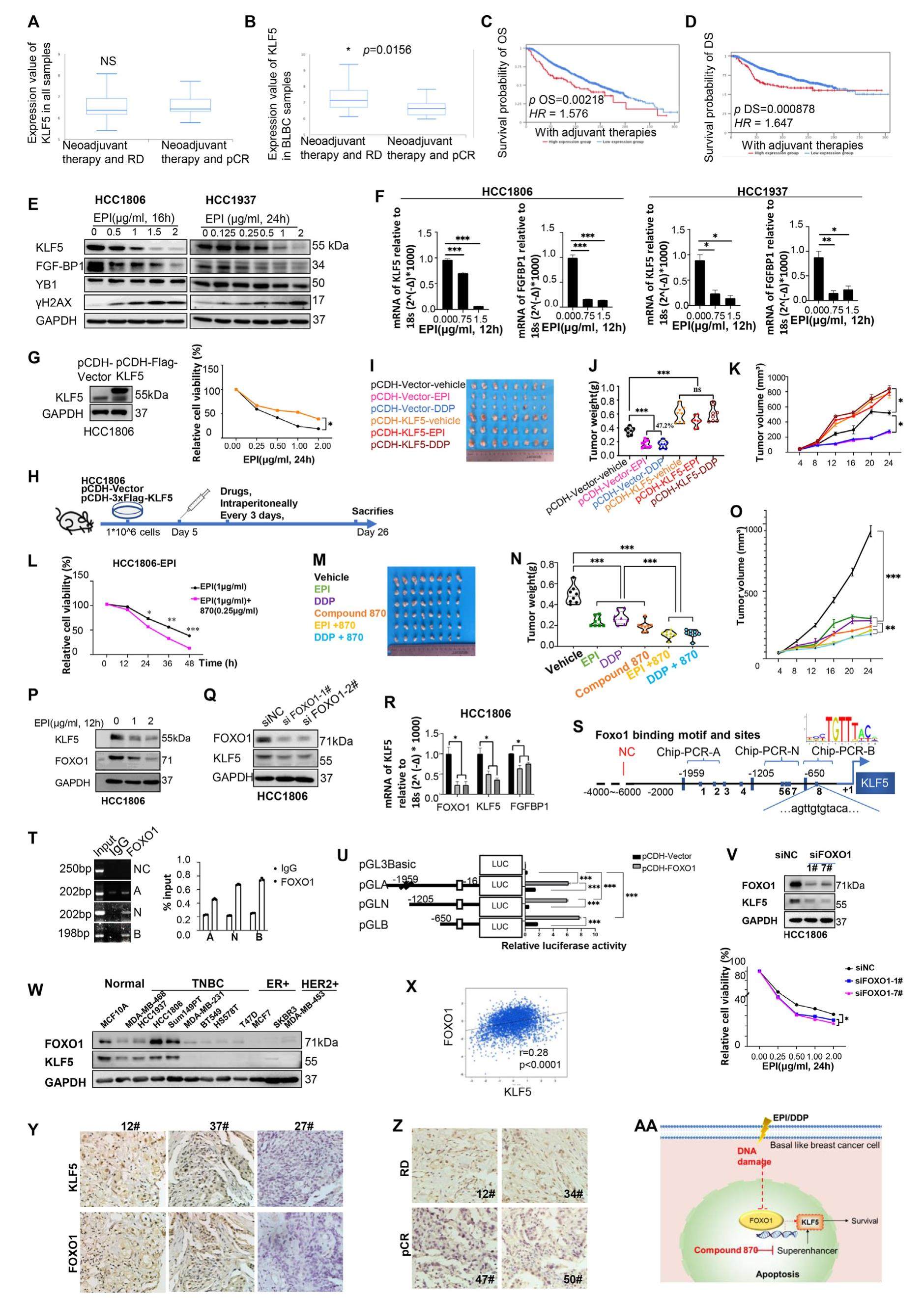
DNA damage chemotherapeutic drugs suppress basal-like breast cancer growth by down-regulating the transcription of the FOXO1-KLF5 axis


Most basal-like breast cancers (BLBCs) have a poor prognosis and high crossover with triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs). However, approximately 50% of TNBC patients develop chemoresistance. Dexamethasone reportedly induces Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) and can cause docetaxel and cisplatin resistance in TNBC. A super-enhancer can maintain the transcription of KLF5. Bromodomain-containing 4 (BRD4) is a transcriptional coactivator in superenhancers, and the BRD4 inhibitor compound 870 could strongly inhibit KLF5 transcription. Forkhead box class O 1 (FOXO1) promotes chemoresistance to doxorubicin in breast cancer. FOXO1 has been shown to promote SOX2 transcription, which plays a critical role in cancer stemness. In addition, FOXO1 promoted KLF5 transcription in diabetic cardiomyopathy. However, the roles of FOXO1 and KLF5 in chemotherapy remain exclusive. In the present study, we examined the function of FOXO1 and the relationship between FOXO1 and KLF5 in BLBCs. We used epirubicin (EPI) and cisplatin (DDP) to treat BLBCs. The expression of FOXO1 and KLF5 was down-regulated, whereas KLF5 overexpression decreased the sensitivity of BLBCs to these drugs. FOXO1 regulated KLF5 in the BLBC chemotherapy response, and a novel therapeutic strategy targeting KLF5 and FOXO1 was proposed.