The role of m6A methylation in female reproductive physiology and pathology


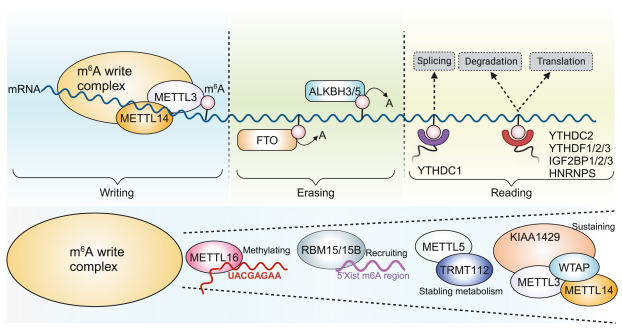
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a critical regulator of female reproductive physiology, yet existing reviews have focused predominantly on oocytes. The objective of this review is to systematically evaluate the regulatory effects of m6A throughout the pregnancy process. This review covers aspects such as oocyte maturation, granulosa cell dynamics, endometrial receptivity, immune homeostasis, and systemic adaptations, aiming to demonstrate the comprehensive regulatory capacity of m6A in female reproduction. Dysregulated m6A modifications in infertility-associated pathologies, including endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, and recurrent miscarriage, are analyzed to identify mechanistic links between an epitranscriptomic imbalance and reproductive dysfunction. The key findings indicate that m6A is involved in the entire reproductive process and precisely coordinates stage-specific molecular programs within it, whereas aberrant methylation patterns disrupt gene networks essential for fertility. Notably, m6A-modifying enzymes exhibit strong potential as diagnostic biomarkers for female reproductive disorders. The synthesis of the current evidence establishes m6A dysregulation as a convergent pathogenic mechanism in diverse infertility etiologies, suggesting that the therapeutic modulation of m6A pathways could address unmet clinical needs in reproductive medicine.