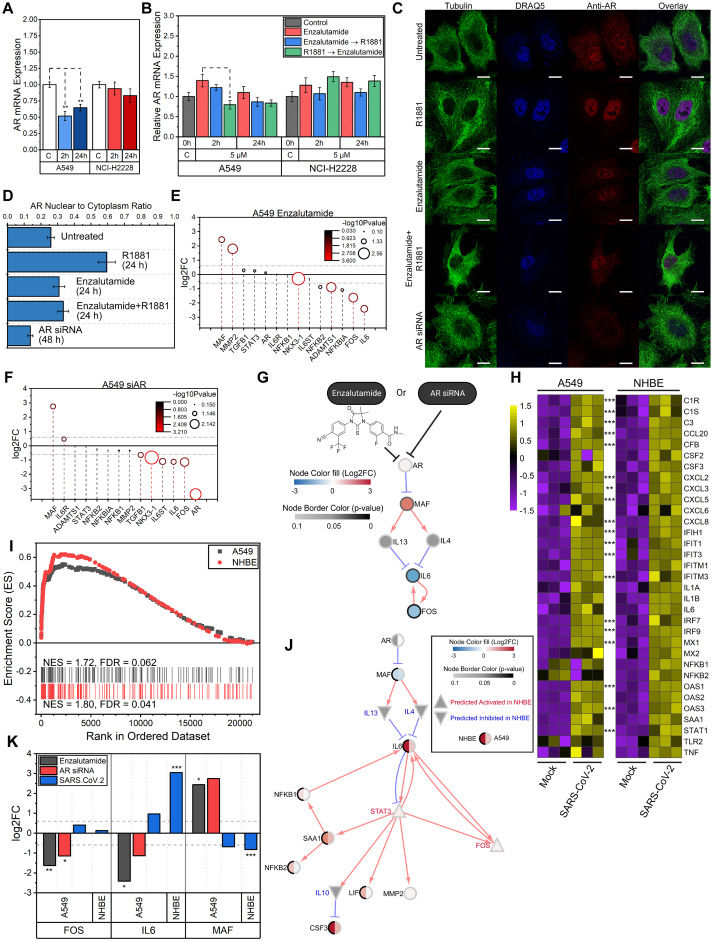
Network analyses: Inhibition of androgen receptor signaling reduces inflammation in the lung through AR-MAF-IL6 signaling axes


Androgen receptor (AR) is a major transcription factor that plays a role in inflammatory response including interleukin-6 (IL6) signaling.1 While AR regulation through paracrine loop signaling in prostate tissue is well-studied, its impact through an IL6 autocrine loop in the lung has not been well-studied despite the organ's response to respiratory viral infection. Chemical inhibition and RNA knockdown of AR identified a bZIP transcription factor MAF to be a common target of inflammation using these perturbations in lung cells. We hypothesized through a predictive in silico network modeling that MAF is a common mediator between androgen signaling and inflammatory response in lung cells exposed to AR antagonists and viral (SARS-Cov-2) infection.