Comprehensive genome sequencing analyses identify novel gene mutations and copy number variations associated with infant developmental delay or intellectual disability (DD/ID)


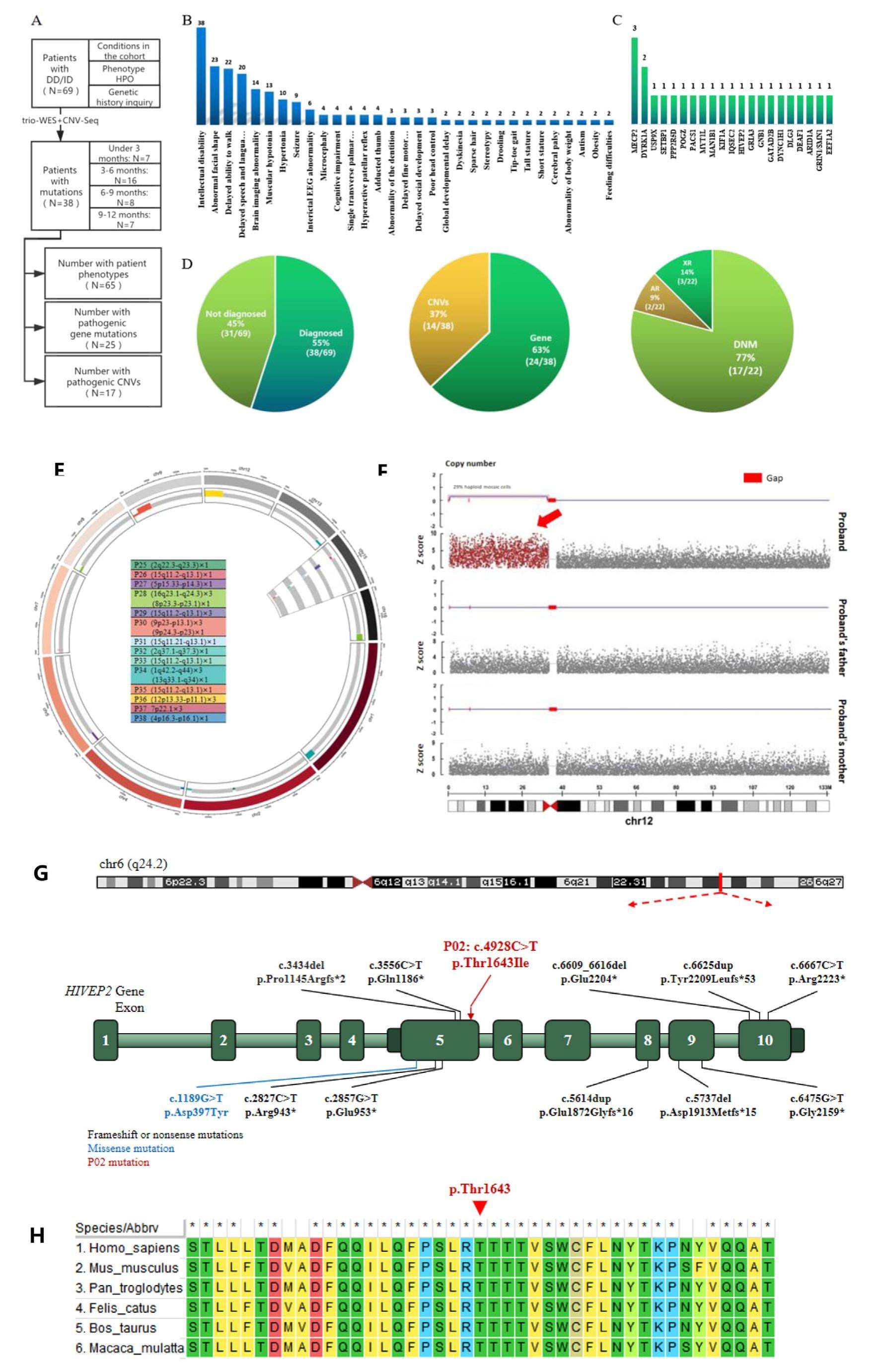
Developmental delay or intellectual disability (DD/ID) is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disabilities worldwide with high clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Its etiology remains unexplained in nearly 70% of these patients, and an accurate diagnosis still poses a challenge in clinical practice. Previous DD/ID cohort studies mostly used panel sequencing or chromosome microarray analysis (CMA), but targeted capture probes could not be updated in time, resulting in an increased risk of missed detection of genetic abnormalities. Whole-exome sequencing (WES) has been proven to result in a high diagnostic yield in patients who present with complex phenotypes. One major limitation of WES for copy number variation (CNV) analysis can be compensated by CNV-Seq technology. In this study, we conducted a retrospective study of the genetic etiology of 69 patients with unexplained DD/ID by using trio-WES and CNV-Seq. The purpose of this study was to analyze the genetic characteristics of DD/ID infants and to explore a rapid, effective, and economical genetic testing regimen.