CD9 role in proliferation, rejuvenation, and therapeutic applications


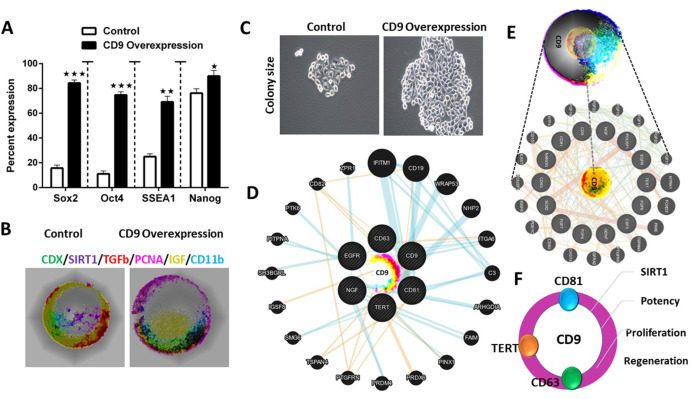
The CD9 gene, also known as the Tspan29 gene, codes for a protein called CD9, which is a member of the tetraspanin family of transmembrane proteins.1 The CD9 protein is involved in various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, and migration.1,2 CD9 has also been found to play a role in the regulation of stem cell proliferation and differentiation.1 Overall, the CD9 gene and its encoded protein play important roles in cellular processes related to proliferation, and further research may uncover new insights into its functions and potential therapeutic applications.1,2 CD9 is involved in a variety of cellular processes that occur at the plasma membrane, including cell adhesion, migration, and signaling.1 It has been shown to interact with other proteins in the plasma membrane, such as integrins, and to modulate their functions.1 CD9 also plays a role in the formation of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains or tetraspanin webs, which are specialized regions of the plasma membrane that are involved in signaling and membrane organization.1 In addition to its role in the plasma membrane of cells, CD9 has also been found in extracellular vesicles, including exosomes, which are released from cells and can play a role in intercellular communication.3 CD9 in exosomes has been shown to play a role in promoting cell adhesion, migration, and invasion in cancer cells.2,3 We overexpressed CD9 in induced pluripotent stem cells and observed high proliferation, enhanced pluripotency, and growth of stem cells. CD9 overexpression has been found to promote cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as resistance to apoptosis.1,4 The effects of CD9 overexpression can vary depending on the specific cell type, the level and duration of overexpression, and other factors.2,5 Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying the effects of CD9 overexpression and its potential therapeutic applications.