Multi-tissue transcriptomics of a unique monozygotic discordant twin case of severe progressive osseous heteroplasia


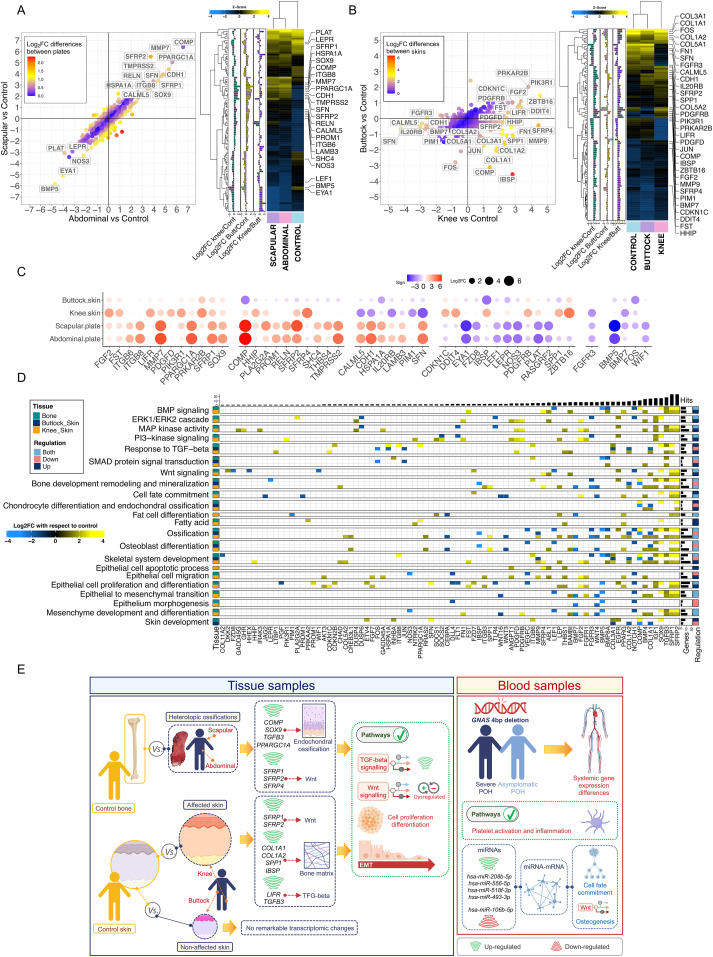
Progressive osseous heteroplasia (POH) is an ultra-rare autosomal dominant disabling disorder characterized by heterotopic ossification (HO). It is caused by heterozygous inactivating mutations in the GNAS (guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-stimulating activity polypeptide) gene. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying HO remain poorly understood. As a treatment for POH is not yet available, the identification of the mechanisms driving POH in affected tissues using gene expression may be of great help to underestand the molecular basis of POH and develop new therapeutic approaches.