Exosomal lncRNA LINC01268 promotes pancreatic cancer progression via the miR-217-KIF2A-PI3K/AKT axis


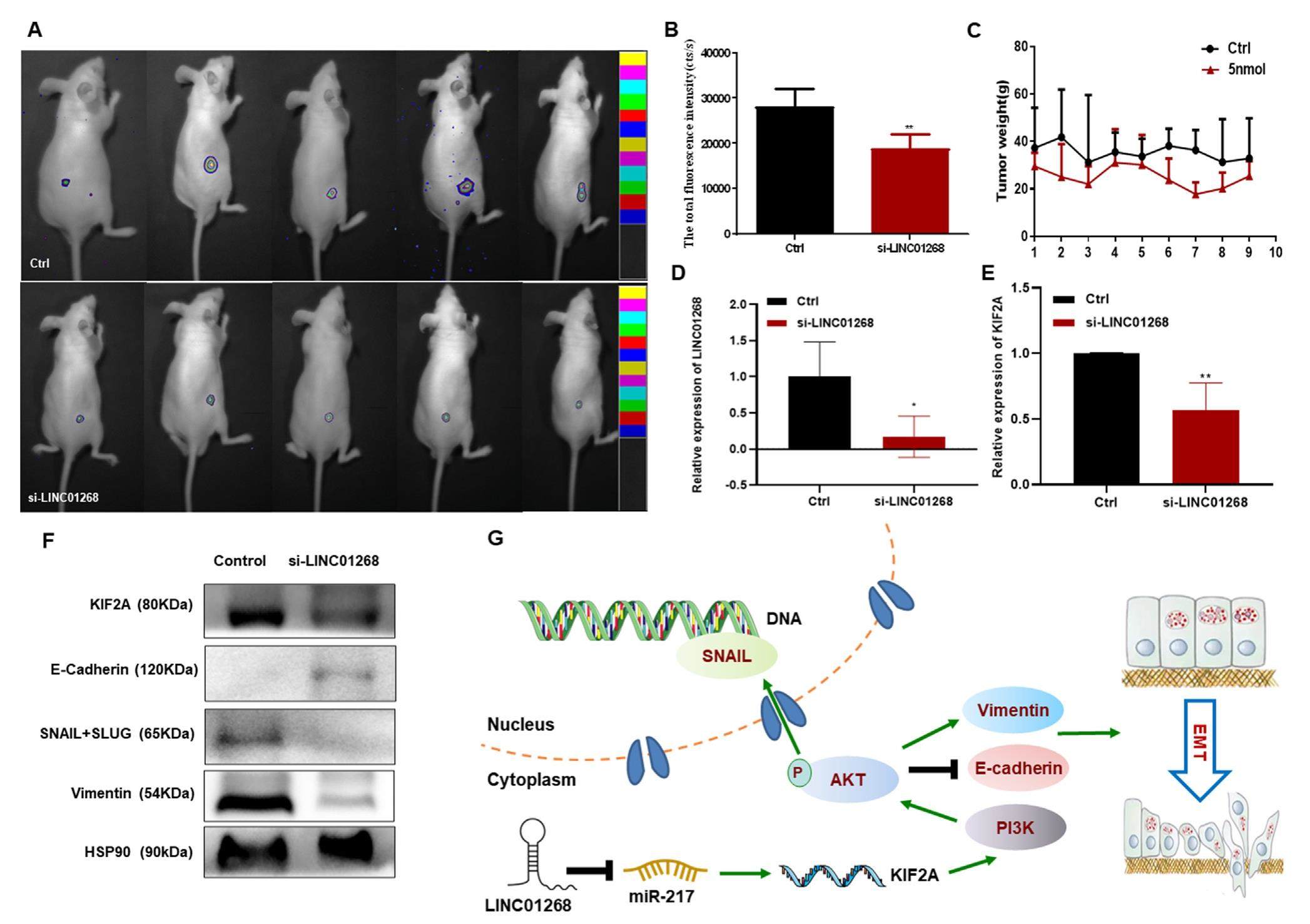
Pancreatic cancer (PaCa) is one of the most aggressive and lethal malignancies with rapid progression and poor prognosis with the 5-year survival rate remaining less than 5% because approximately 80% of PaCa patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage and lose the chance of curative resection. Accumulated evidence has revealed that noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are involved in the pathogenesis of PaCa and serve as potential biomarkers for PaCa. Exosomal lncRNAs also play a vital role in tumorigenesis and some exosomal lncRNAs have been reported to accelerate tumor progression. In this study, we first employed RNA-seq of PaCa plasma samples to identify significantly differentially expressed lncRNAs in PaCa patients and revealed that LINC01268 was up-regulated in PaCa tumor tissues and plasma. LINC01268 is an emerging lncRNA associated with glioma malignancy grade. Thus. we further analyzed the malignant biological behaviors of this lncRNA in PaCa and found that LINC01268 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion as an oncogene, which promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in PaCa via the miR-217-KIF2A-PI3K/AKT axis.