Identification and functional analysis of CCN6 variants in progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia: Exploring the potential role of ferroptosis and apoptosis in chondrocytes


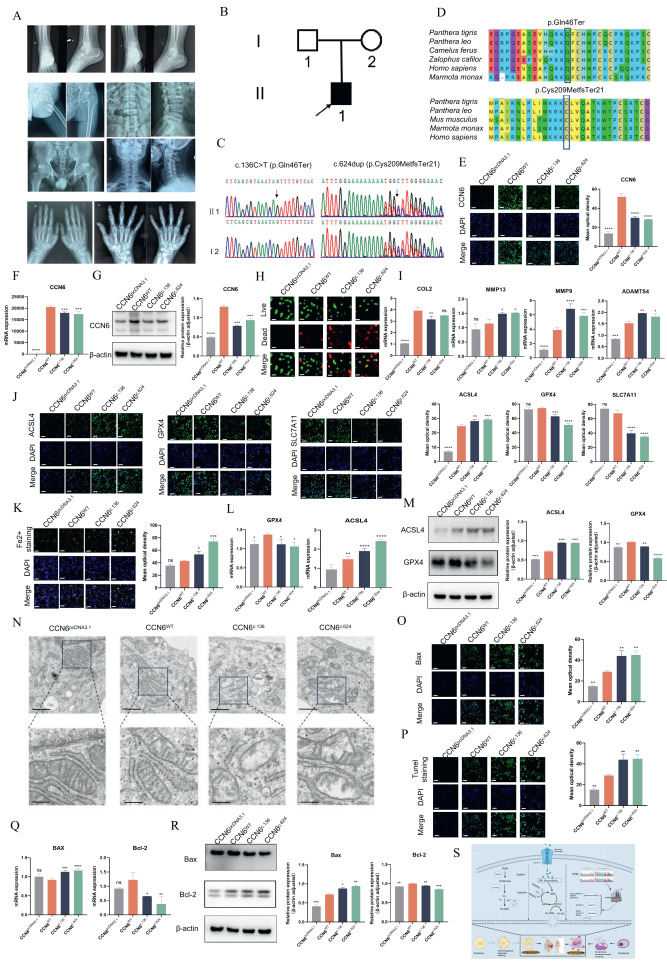
Progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia (PPD, MIM 603400) is a rare autosomal recessive skeletal disorder that profoundly impairs joint function and diminishes quality of life. It is characterized by disproportionate short stature, extensive cartilage damage, and progressive joint enlargement symptoms typically including joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, initially affecting the interphalangeal joints before progressively involving larger joints and the spine.1 This progression often leads to severe joint contractures, spinal deformities, and gait abnormalities, significantly restricting mobility and overall well-being. The complexity of these complications highlights the critical role of genetic analysis in achieving an accurate diagnosis.2