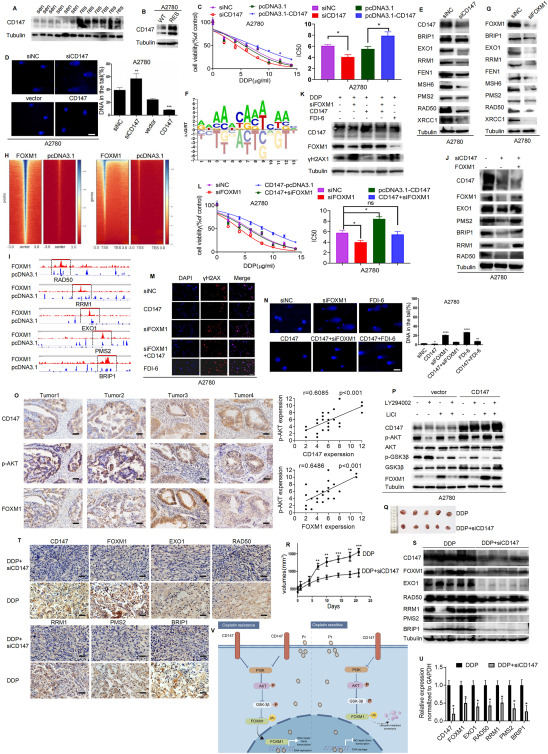
CD147 facilitates cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer through FOXM1 degradation inhibition


Currently, the major therapy for patients with ovarian cancer includes post-cytoreductive surgery followed by chemotherapy of carboplatin or cisplatin plus paclitaxel. The rise of drug resistance is a substantial factor in cancer recurrence and mortality among ovarian cancer patients receiving cisplatin treatment. CD147 is widely expressed in a variety of cancer tissues1 and recognized as a drug target for its antibody drug Licartin which has been approved by China's National Medicines and Pharmaceutical Administration.2 Even though many studies reported that CD147 is involved in the cisplatin resistance of varieties of cancers,3 its mechanism remains unclear. In this investigation, we uncovered a distinctive mechanism by which CD147 regulates cisplatin resistance through the proteasomal degradation of the transcription factor FOXM1, which is associated with DNA damage repair, in ovarian cancer cells. Our results suggest that targeting CD147 may have therapeutic implications for increasing cisplatin efficiency in the management of ovarian cancer.