Whole exome sequencing identifies new susceptibility candidates underlying community-acquired pneumonia


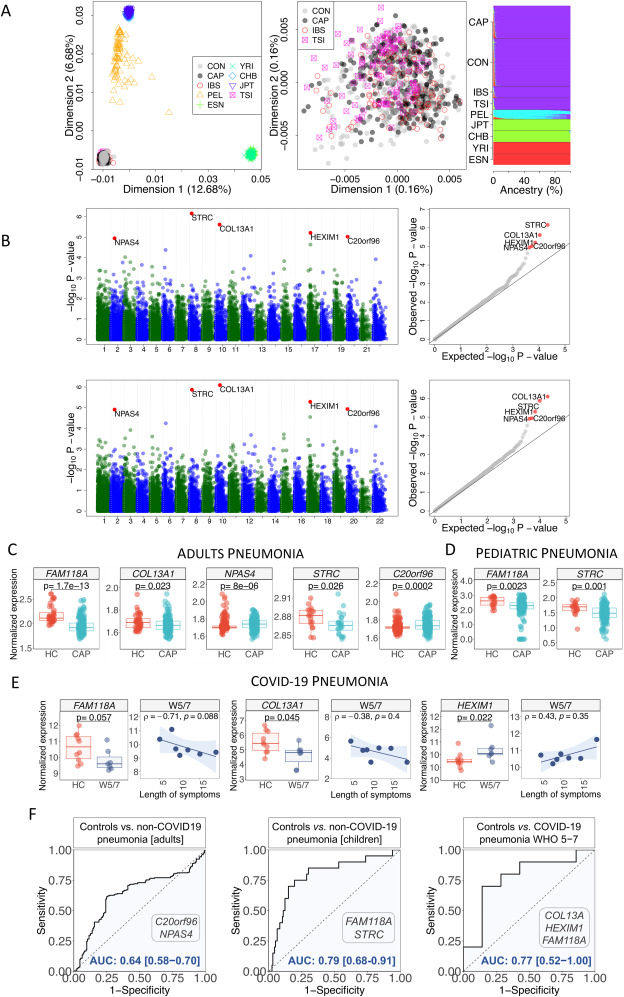
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung with symptoms that include productive dry cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing, and it is usually caused by viruses and bacteria, but also other microorganisms (such as fungi and parasites). Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a major cause of infectious diseases, hospitalization, and mortality, especially in the elderly population.1 We have undertaken a case–control study on CAP patients by way of sequencing the complete exome of 300 patients and 438 healthy controls (Table S1 for demographic and clinical characteristics of patients). This study is by far the largest exome sequencing project to date aimed at exploring the potential genetic causes behind CAP.