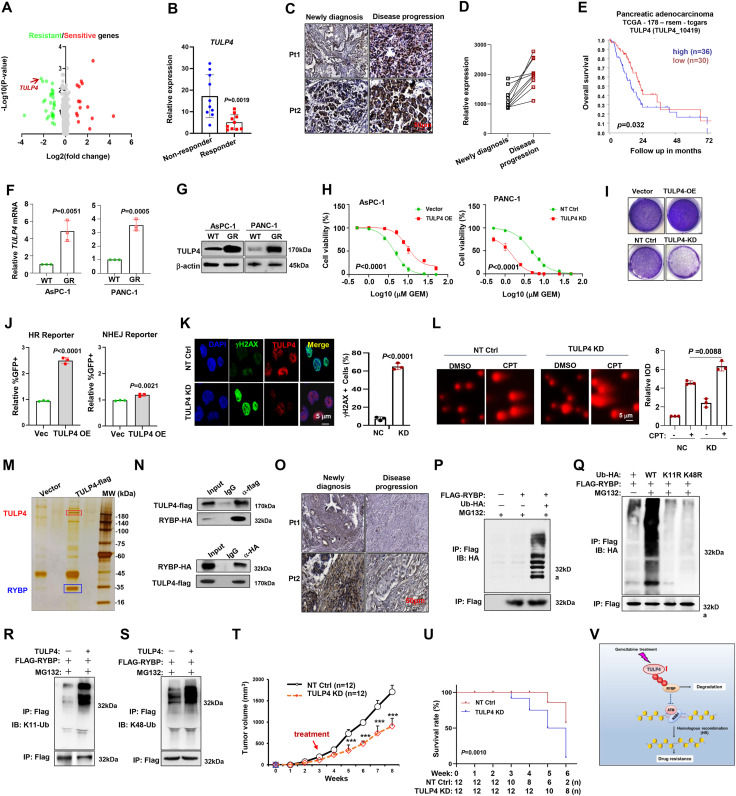
TULP4 degrades RYBP to enhance DNA damage repair and chemosensitivity of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma


Gemcitabine is widely used in the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), but the development of chemoresistance poses a significant challenge to achieving long-term disease-free survival in PDAC patients.1 Resistance to gemcitabine may arise from various cellular and molecular changes in metabolism, tumor microenvironment, and DNA damage repair efficiency.2 Despite existing knowledge, large-scale molecular mechanisms underlying gemcitabine resistance remain unclear. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to more effective treatment strategies for this highly aggressive disease.