The USP7 protein interaction network and its roles in tumorigenesis


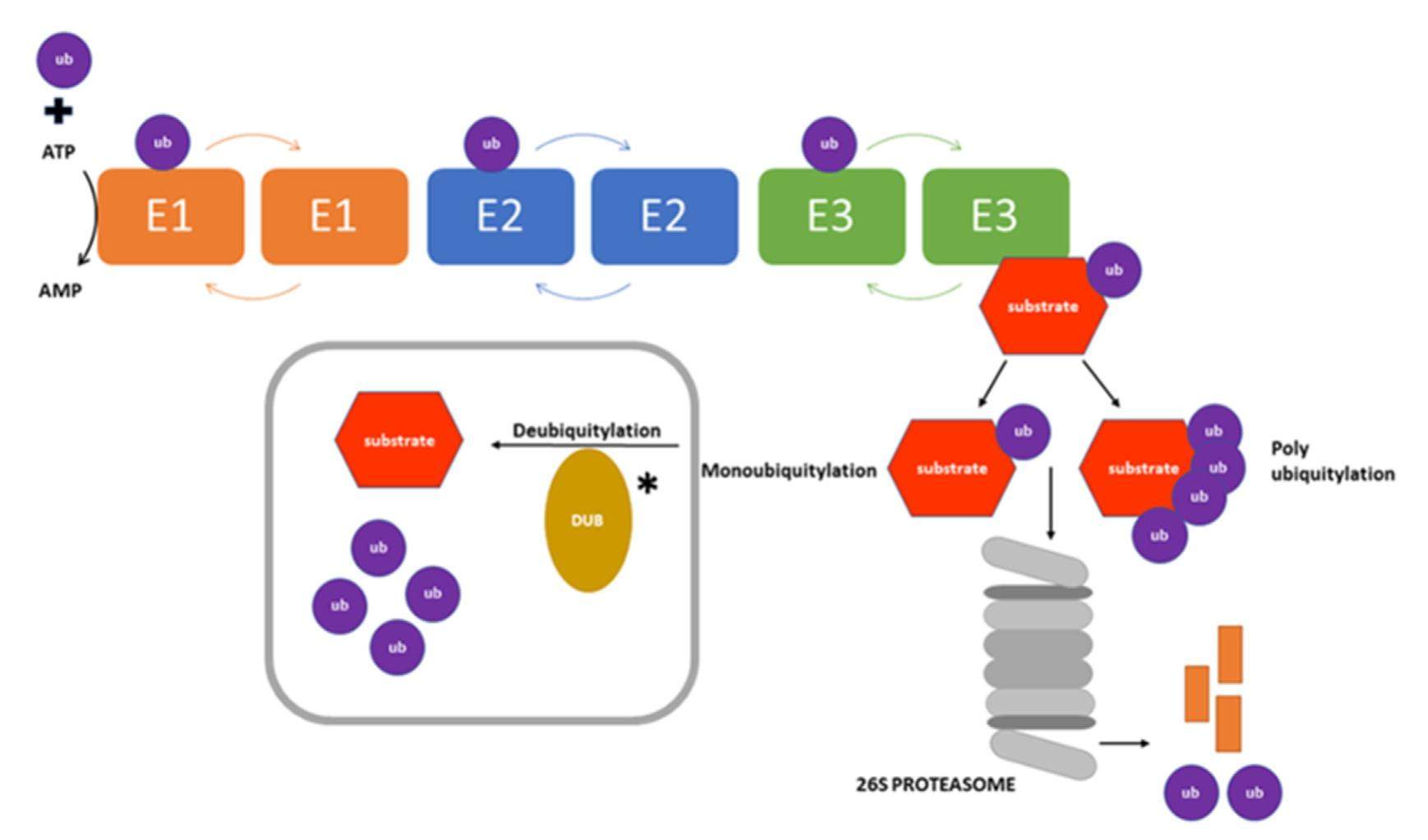
Ubiquitin-specific protease (USP7), also known as Herpesvirus-associated ubiquitinspecific protease (HAUSP), is a deubiquitinase. There has been significant recent attention on USP7 following the discovery that USP7 is a key regulator of the p53-MDM2 pathway. The USP7 protein is 130 kDa in size and has multiple domains which bind to a diverse set of proteins. These interactions mediate key developmental and homeostatic processes including the cell cycle, immune response, and modulation of transcription factor and epigenetic regulator activity and localization. USP7 also promotes carcinogenesis through aberrant activation of the Wnt signalling pathway and stabilization of HIF-1α. These findings have shown that USP7 may induce tumour progression and be a therapeutic target. Together with interest in developing USP7 as a target, several studies have defined new protein interactions and the regulatory networks within which USP7 functions. In this review, we focus on the protein interactions of USP7 that are most important for its cancer-associated roles.