Characterization of the essential role of bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) through RNA interference


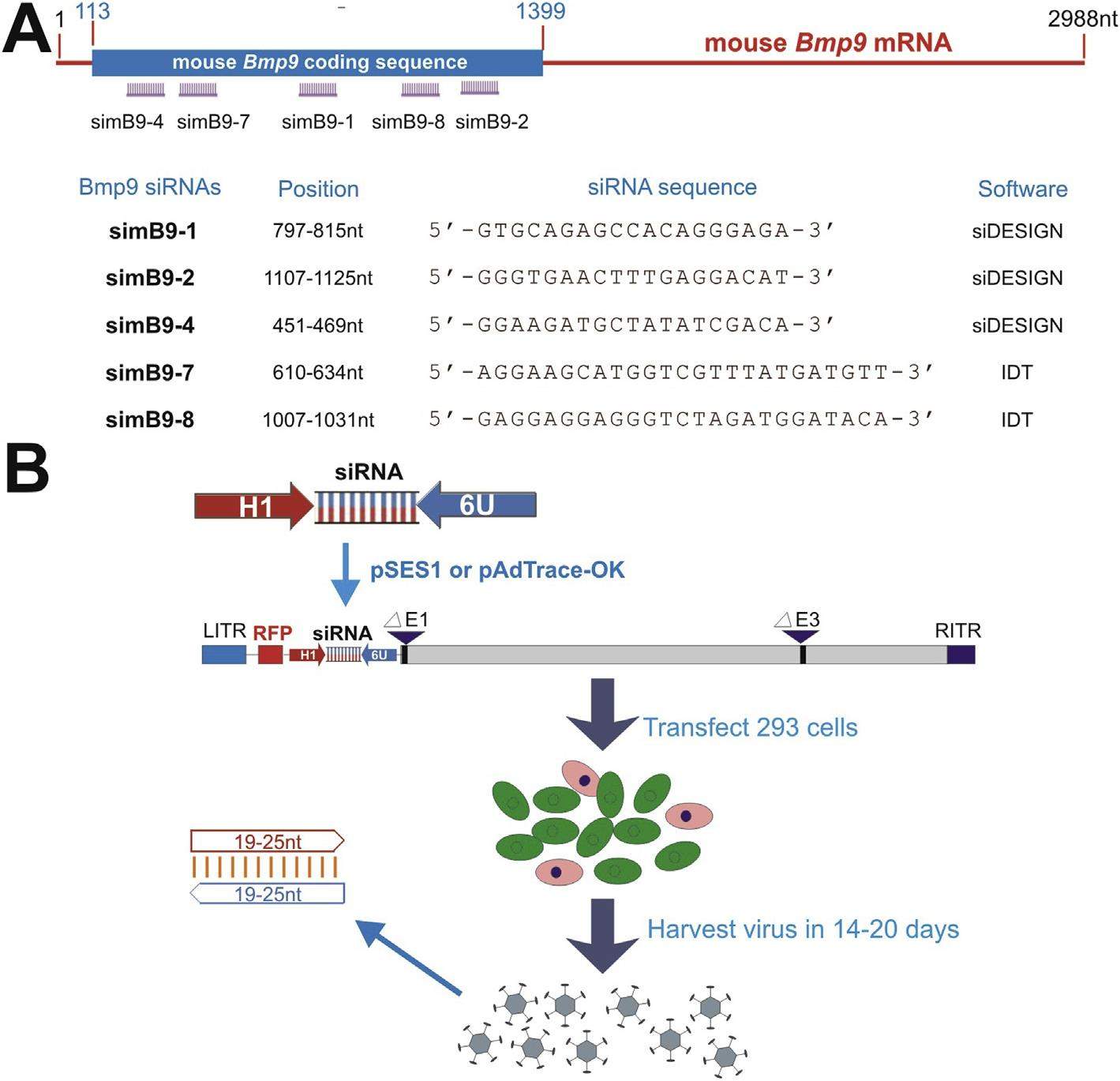
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent stem cells and capable of differentiating into multiple cell types including osteoblastic, chondrogenic and adipogenic lineages. We previously identified BMP9 as one of the most potent BMPs that induce osteoblastic differentiation of MSCs although exact molecular mechanism through which BMP9 regulates osteogenic differentiation remains to be fully understood. Here, we seek to develop a recombinant adenovirus system to optimally silence mouse BMP9 and then characterize the important role of BMP9 in osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. Using two different siRNA bio-informatic prediction programs, we design five siRNAs targeting mouse BMP9 (or simB9), which are expressed under the control of the converging H1 and U6 promoters in recombinant adenovirus vectors. We demonstrate that two of the five siRNAs, simB9-4 and simB9-7, exhibit the highest efficiency on silencing exogenous mouse BMP9 in MSCs. Furthermore, simB9-4 and simB9-7 act synergistically in inhibiting BMP9-induced expression of osteogenic markers, matrix mineralization and ectopic bone formation from MSCs. Thus, our findings demonstrate the important role of BMP9 in osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. The characterized simB9 siRNAs may be used as an important tool to investigate the molecular mechanism behind BMP9 osteogenic signaling. Our results also indicate that recombinant adenovirus-mediated expression of siRNAs is efficient and sustained, and thus may be used as an effective delivery vehicle of siRNA therapeutics.