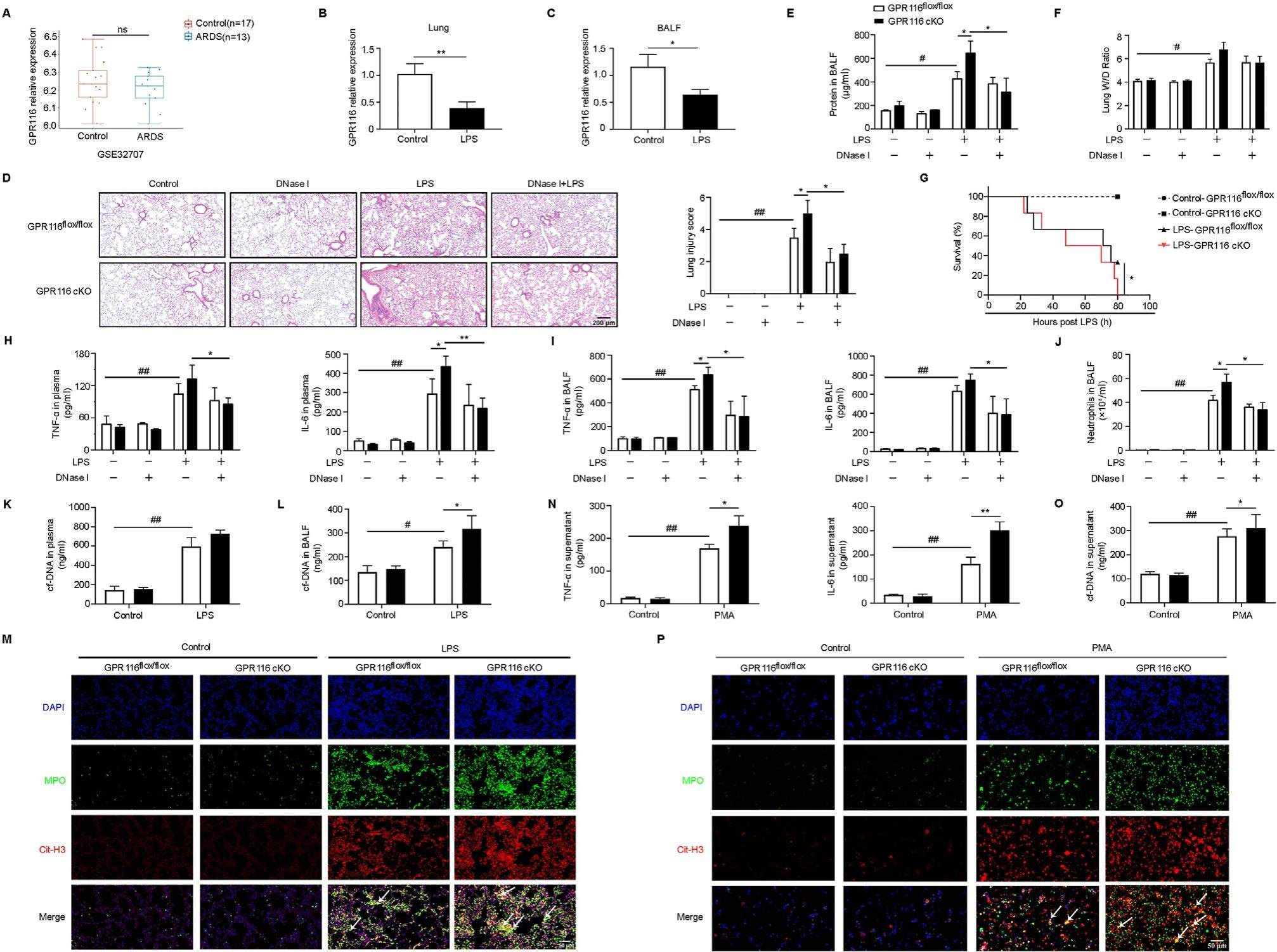
Deletion of G protein-coupled receptor 116 enhances neutrophil function and aggravates lung injury in mice


Acute lung injury (ALI) globally afflicts over 3 million individuals every year. It can eventually develop into acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with a high mortality of up to 40%.To date, ALI has been undertreated in terms of the feeble efficacy of clinical approaches and the lack of proven pharmacological targets. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), the promising targets of modern medicine, participate intensively in the regulation of human physiology and pathophysiology. Among them, Gpr116, which is expressed in alveolar epithelial cells and immune cells, has been reported to play a key role in maintaining alveolar homeostasis and inhibiting inflammation. However, its role in the regulation of neutrophil function and ALI remains to be elucidated. In this study, we demonstrated the inhibitory role of Gpr116 on neutrophil function, which contributes to nonspecific lung injury in mice induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).