SIGLEC15 modulates the immunosuppressive microenvironment and suppresses malignant phenotypes in triple-negative breast cancer


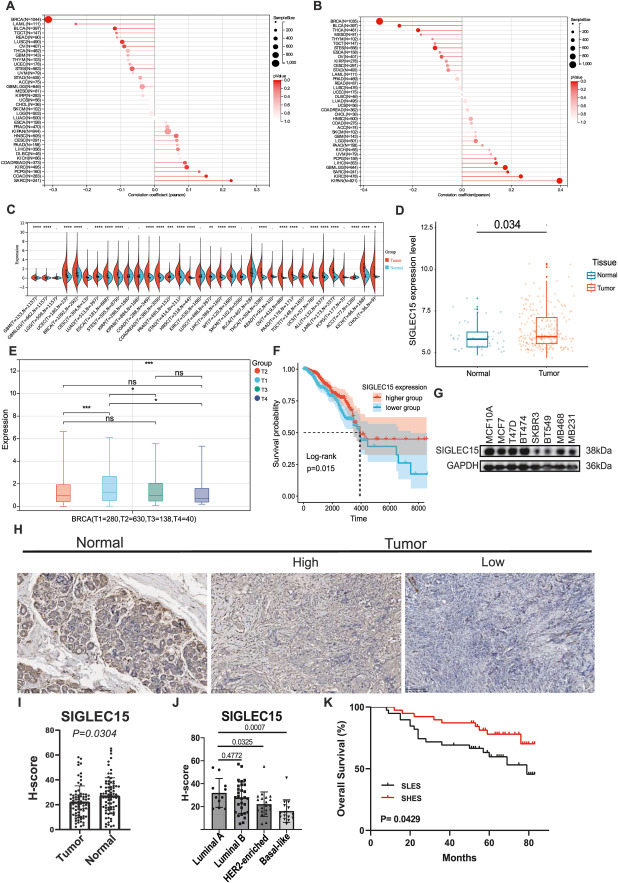
Previous studies have demonstrated a significant association between sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 15 (SIGLEC15) and both the progression of malignant tumors and immune infiltration. This study comprehensively analyzed and elaborated the function and related mechanism of SIGLEC15 in breast cancer. We analyzed SIGLEC15 expression levels and predicted its functions using mRNA sequencing in a population-based dataset. Single-cell RNA sequencing was utilized to investigate the biological roles of SIGLEC15 within the tumor microenvironment (TME). Finally, we conducted both in vivo and in vitro experiments to validate the findings derived from the RNA sequencing analyses. Elevated SIGLEC15 expression was associated with favorable outcomes in breast cancer patients. Tumor cells exhibiting high SIGLEC15 expression demonstrated reduced epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) tendencies compared to those with lower expression levels, potentially through the regulation of ZEB1 expression. However, anti-tumor immunity was significantly suppressed in the TME containing these tumor cells. Analysis of protein expression in patient samples revealed a negative correlation between SIGLEC15 expression and CD4, CD8 T-cell infiltration. In mouse models, tumor cells overexpressing SIGLEC15 exhibited diminished invasive and migratory capabilities. Furthermore, both in vitro and in vivo experiments confirmed that Nutlin-3a has a more pronounced inhibitory effect on breast cancer cells with elevated SIGLEC15 expression. The expression level of SIGLEC15 can serve as a biomarker to assess the malignancy of breast cancer and the degree of immune infiltration. Monitoring SIGLEC15 expression levels can facilitate more informed and personalized clinical decision-making for the treatment of breast cancer patients.