Role of angiogenesis-related lncRNAs in tumor microenvironment and prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma


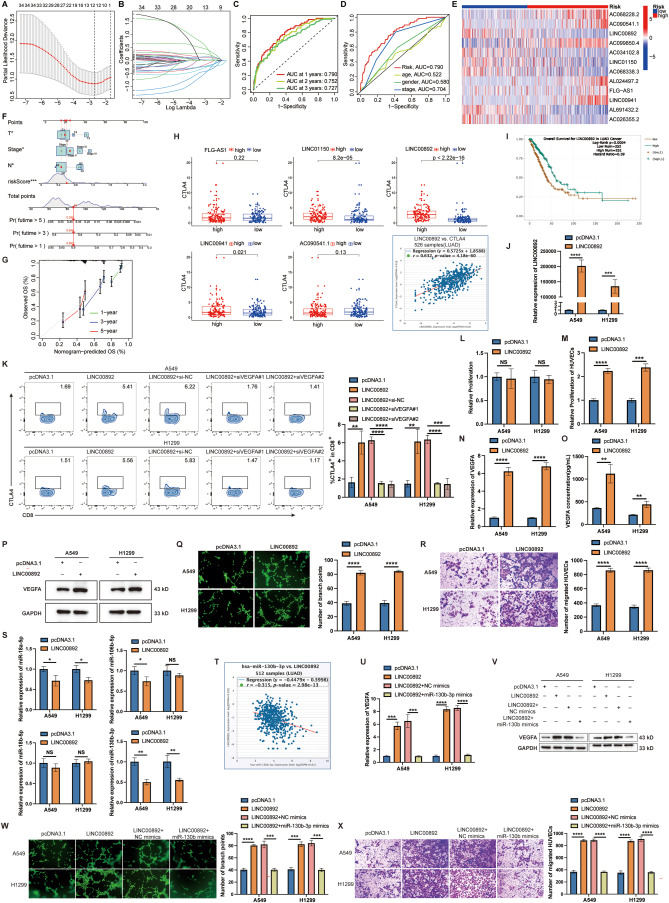
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), especially angiogenesis-related lncRNAs (ARLncs), are vital cancer biomarkers.1,2 This study explores their role in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), focusing on their influence on the tumor environment and angiogenesis. We identified 12 ARLncs to develop a prognostic signature independent of conventional indicators for LUAD patients. Notably, the low-risk group showed better outcomes, higher cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA4) expression, and improved response to CTLA4 checkpoint inhibitors. LINC00892 stood out as a key regulator of CTLA4 expression, linked to increased levels via vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA). LINC00892 overexpression in LUAD cells boosted human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation and migration by sponging miR-130b-3p and controlling VEGFA. This study introduces an innovative ARLncs-based prognostic model for LUAD, highlighting LINC00892's role in modulating CTLA4 expression through VEGFA, potentially guiding immunotherapy strategies for LUAD.