The role of SOX transcription factors in prostate cancer: Focusing on SOX2


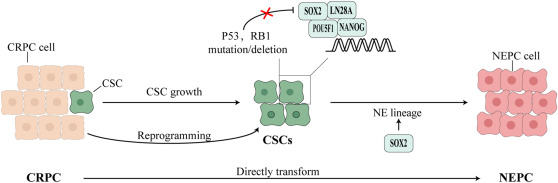
Prostate cancer remains a major health problem, with its incidence ranking second among male malignancies worldwide. Recent studies have highlighted the critical role of the SOX family transcription factors, especially SOX2, in prostate cancer pathogenesis. SOX2 regulates the fate of cancer stem/progenitor cells, contributing to tumor initiation, development, and metastasis. Elevated SOX2 levels have been detected in prostate cancer tissues and are associated with higher tumor grade, aggressive phenotype, and poor prognosis. SOX2 also impacts various tumor biological behaviors, including cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, resistance to apoptosis, and treatment resistance. This review highlights the role of SOX proteins in prostate cancer, focusing on the molecular mechanisms by which SOX2 drives cancer progression, elucidating the mechanisms controlling its activity, and emphasizing its potential as a therapeutic target.