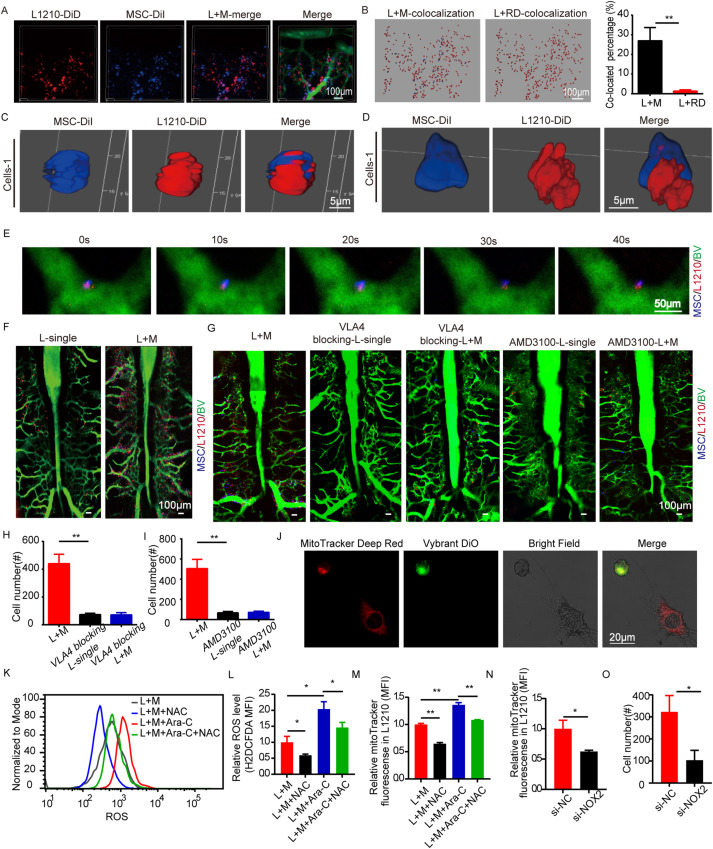
Bone marrow mesenchymal stroma cell serves as a harbor anchoring acute B lymphoblastic leukemia cells


A growing body of evidences suggests that mesenchymal stroma cells (MSCs) are not only a therapeutic resource to treat various diseases, but also an important pathogenic worker in tumorigenesis.1 However, the differences between in vitro and in vivo environment draw the major concern leading to the contradictory effects of MSCs on tumorigenesis.2 Technical limitation makes it even hard to dissect the real cell–cell interacting model in a living status. As like a two-edge sword, dissecting the underlying mechanism resulting in this dilemma would help to apply MSCs more accurately in translational medicine. In our study, we applied murine in vivo calvarium intravital microscopy (IVM) and in vivo flow cytometry (IVFC) to directly observe the dynamic cell–cell interaction between acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells (L1210s) and BM (bone marrow)-MSCs. Our data clarified a living model by which BM-MSCs provide a micro-niche to facilitate leukemia cells invasion.