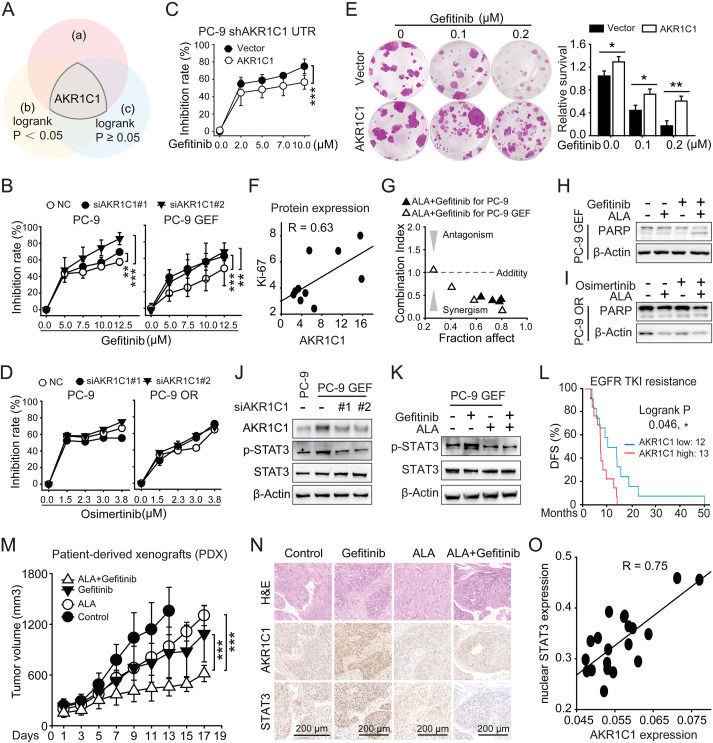
The targeting of AKR1C1 synergizes with gefitinib via the STAT3 signaling pathway in EGFR-mutated NSCLC


As the first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR-TKI), gefitinib has been proven effective for patients with Del19 or L858R mutations in EGFR. Secondary mutations in EGFR (mainly T790M) confer resistance to gefitinib in ∼50% of patients.1 However, resistance still occurs in other patients without secondary mutations in EGFR, which indicates that EGFR-independent mechanisms also play a vital role in the gefitinib resistance cascade, which deserves further investigation. Our previous studies have demonstrated that aldo-keto reductase 1C1 (AKR1C1) promotes non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) metastasis by directly interacting with signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) and reinforcing its activity.2 Although studies have focused on the protumor roles of AKR1C1, the role of AKR1C1 in gefitinib resistance is still unknown.