Hub genes identification for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease in patients with Crohn's disease


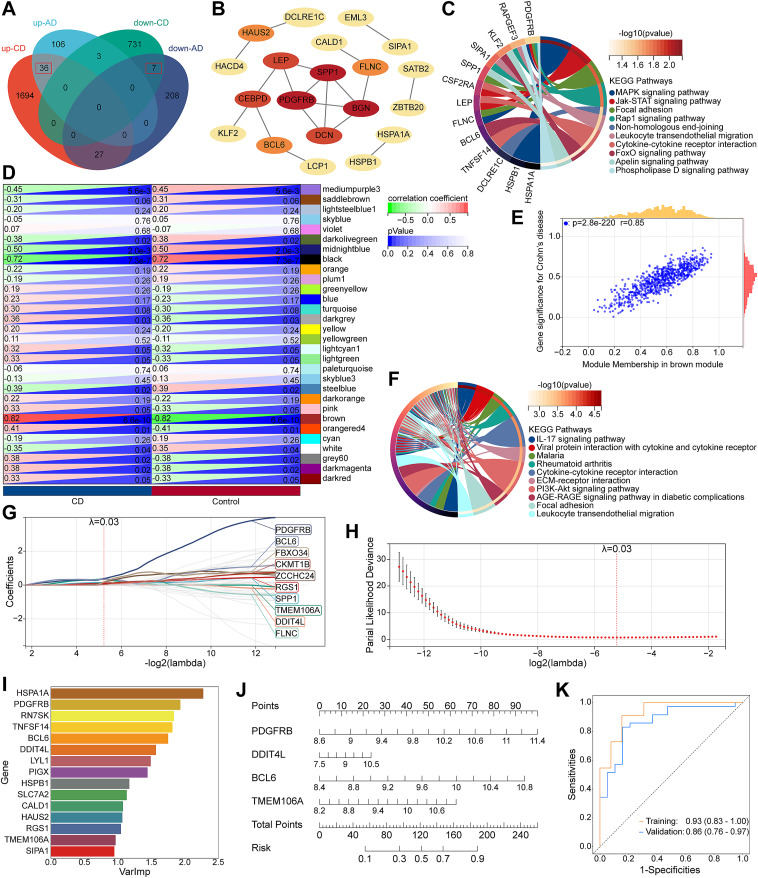
Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains clinically incurable, raising a significant public health issue, particularly with its continuously increased incidence.1 Inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease (CD), is characterized by long-standing inflammation and immunological imbalance of the gastrointestinal system.2 Recent epidemiological studies suggest a link between increased AD risk and inflammatory bowel disease.3,4 Due to the unclear regulatory mechanism potentially connecting AD with inflammatory bowel disease, this study is designed to reveal the underlying mechanisms at the genetic level and identify diagnostic markers to predict the risk of developing AD in patients with CD. Gene expression data of AD (GSE109887) and CD (GSE95095) were obtained from the GEO database for further bioinformatics analyses, including differentially expressed gene (DEG) identification, weighted gene co-expression network analysis, protein–protein interaction network construction, enrichment analyses, and immune infiltration. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was employed to filter hub genes in conjunction with another machine learning algorithm, random forest. Then, a nomogram was constructed and validated to assess the diagnostic value. Consequently, we identified four hub genes (PDGFRB, BCL6, DDIT4L, TMEM106A) strongly related to AD with CD, and constructed a credible diagnostic model based on these genes. Distinct but interrelated pathways were revealed in the pathological process of AD with CD, providing new perspectives on the molecular mechanisms linking these two diseases and underscoring the importance of further investigation of these shared genetic pathways. Moreover, the developed nomogram could assist clinical decision-making and highlight potential therapeutic targets for AD in CD patients. Figure S1 provides a concise overview of our research process.