HMGN2 accelerates the proliferation and cell cycle progression of glioblastoma by regulating CDC20 expression


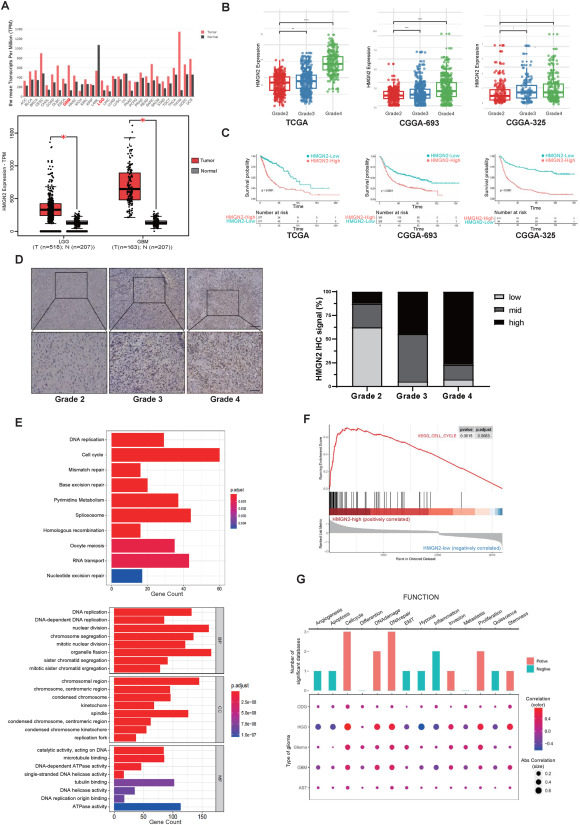
Gliomas represent the most common primary malignant intracranial tumors in adults. Despite recent advances in treatment, the prognosis of patients with glioblastoma remains poor. Epigenetic abnormalities, the hallmarks of various types of cancer, contribute to the dysregulated expression of cancer-related genes. Post-translational modification of histones plays a pivotal role in cancer development and progression by modulating gene transcription, chromatin remodeling, and nuclear structure. Therefore, further exploration of the molecular mechanisms of epigenetic regulation in gliomas and the identification of superior therapeutic targets are required. High-mobility group nucleosomal-binding domain 2 (HMGN2) participates in the epigenetic regulation of genes through histone modification and exhibits significant differential expression between glioma and normal tissues. However, the effect of HMGN2 on gliomas and its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to elucidate these uncertainties by demonstrating that HMGN2 significantly promotes the proliferation of glioma cells. HMGN2 binds to histones and promotes the stability of H3K27ac acetylation in the cell division cycle 20 (CDC20) promoter region, enhancing the transcriptional activity of CDC20 and increasing the proliferation of glioma cells. Moreover, we found that CDC20 expression was negatively correlated with the survival time of patients with glioma. These results suggest that targeting epigenetic regulation, such as the HMGN2/CDC20 axis, may provide a novel direction for the treatment of gliomas.