Latitudinal and longitudinal regulation of tissue macrophages in inflammatory diseases


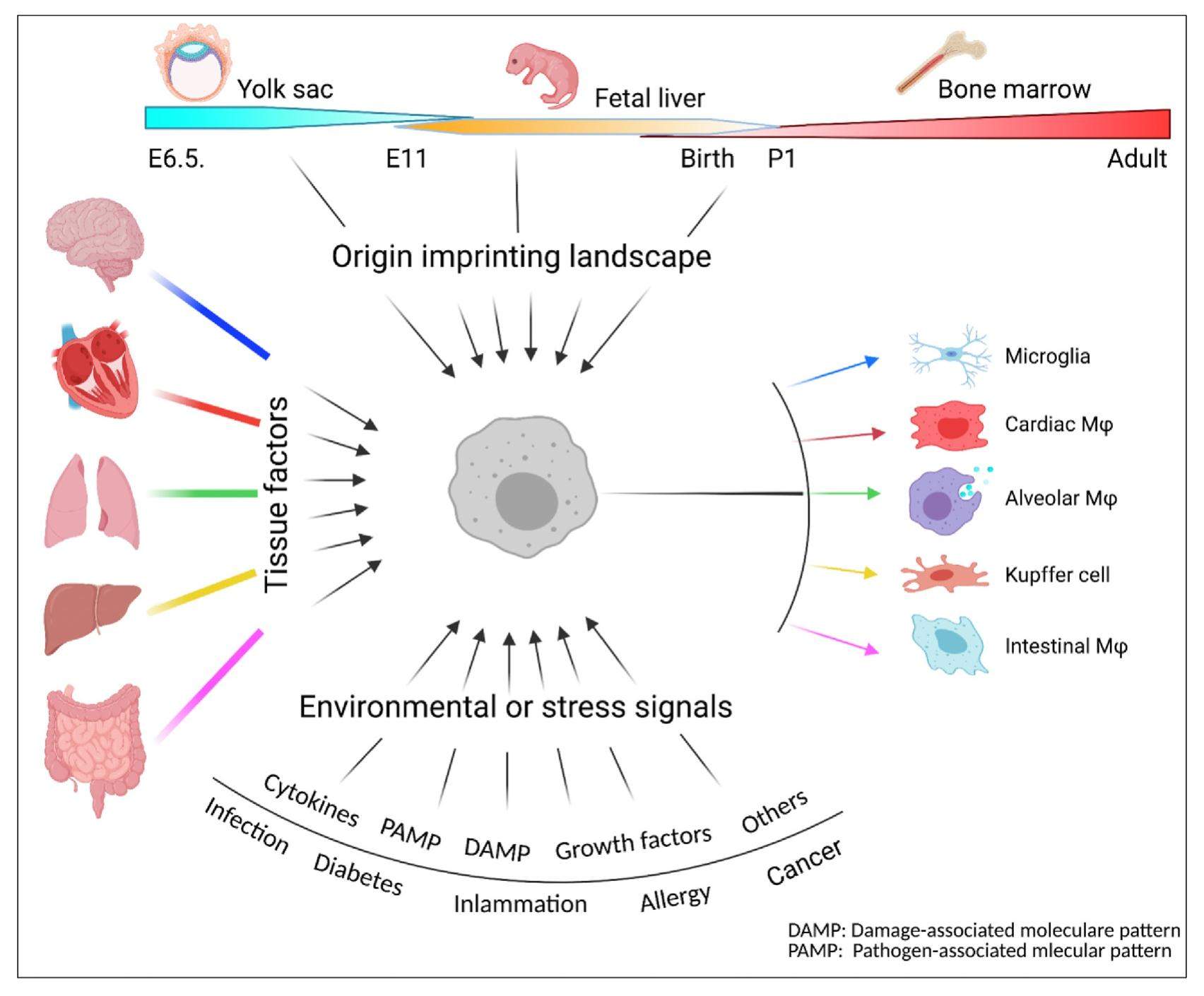
Macrophages are dominant innate immune cells. They demonstrate remarkable heterogeneity and plasticity that are essential for homeostasis and host defense. The heterogeneity of tissue macrophages is shaped by the ontogeny, tissue factors, and environmental signals, a pattern in a tissue-associated latitudinal manner. At the same time, macrophages have long been considered as mainly plastic cells. These cells respond to stimulation quickly and in a stimulusspecific way by utilizing a longitudinal cascaded activation, including coordination of signal transducer, epigenetic elements, and transcription factors, conclusively determine the macrophage phenotypes and functions. With the development of cutting-edge technologies, such as fatemapping, single-cell transcriptomics, ipsc platform, nanotherapeutic materials, etc., our understanding of macrophage biology and the roles in the pathogenesis of diseases is much advanced. This review summarizes recent progress on the latitudinal and longitudinal regulation of tissue macrophages ininflammatory diseases. The latitudinal regulation covers the tissuemacrophage origins, tissue factors, and environmental signals, reflecting themacrophage heterogeneity. The longitudinal regulation focuses on how multiple factors shape the phenotypes and functions of macrophage subsets to gain plasticity in inflammatory diseases (i.e., inflammatory bowel disease). In addition, how to target macrophages as a potential therapeutic approach and cutting edgetechnologies for tissue macrophage study are also discussed in this review.