Transcription factors, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, and therapeutic implications


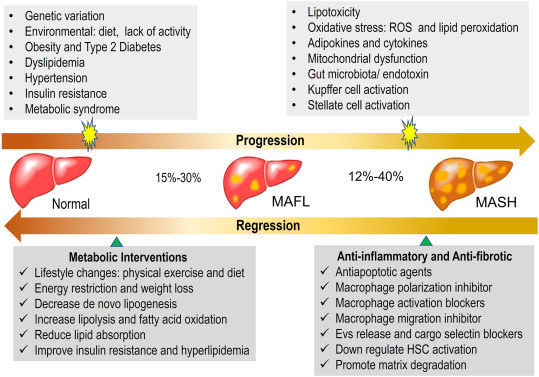
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) encompasses a spectrum of liver diseases ranging from metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, which may progress to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Several mechanisms, including obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, inflammation, apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and reactive oxygen species, have been proposed to underlie the progression of MAFLD. Transcription factors are proteins that specifically bind to DNA sequences to regulate the transcription of target genes. Numerous transcription factors regulate MAFLD by modulating the transcription of genes involved in steatosis, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis. Here, we review the pathological factors associated with MAFLD, with a particular emphasis on the transcription factors that contribute to the progression of MAFLD and their therapeutic implications.