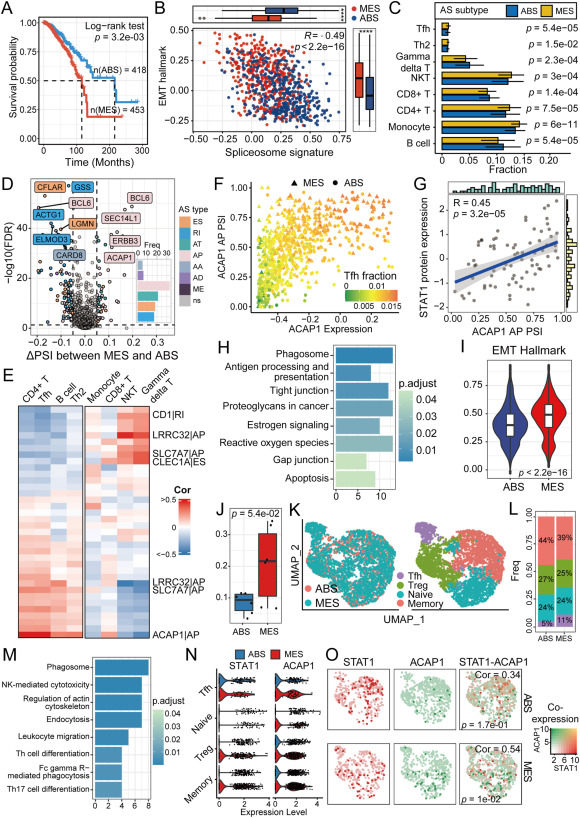
Alternative splicing of immune-related genes identifies breast cancer subtypes with differential immune cell infiltration


Breast cancer, recognized as a foremost cause of mortality among women, is characterized by a complex immune microenvironment. Alternative splicing (AS) is a crucial process leading to diverse transcript variants. Studies have shown AS's role in T cell and B cell stimulation. For instance, Shalek et al performed single-cell RNA sequencing and showed that different AS patterns existed depending on the maturity and differentiation of dendritic cells, such as Cxcl10.1 AS of CD28 enhances the viability of activated T cells.2 However, the role of AS in breast cancer, particularly in relation to immune cell infiltration, remains underexplored.