Cardiomyocyte proliferation: Advances and insights in macrophage-targeted therapy for myocardial injury


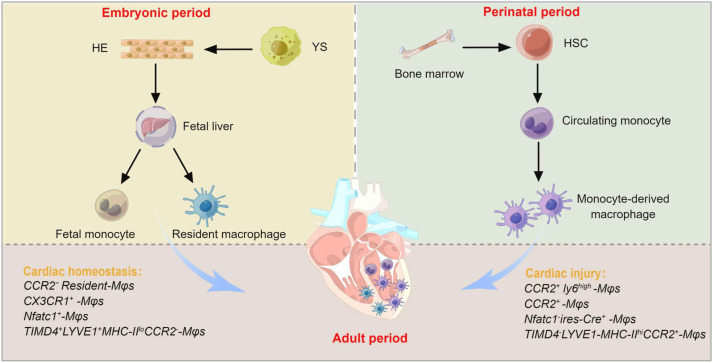
n the mammalian heart, cardiomyocytes undergo a transient window of proliferation that leads to regenerative impairment, limiting cardiomyocyte proliferation and myocardial repair capacity. Cardiac developmental patterns exacerbate the progression of heart disease characterized by myocardial cell loss, ultimately leading to cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. Myocardial infarction causes the death of partial cardiomyocytes, which triggers an immune response to remove debris and restore tissue integrity. Interestingly, when transient myocardial injury triggers irreversible loss of cardiomyocytes, the subsequent macrophages responsible for proliferation and regeneration have a unique immune phenotype that promotes the formation of pre-existing new cardiomyocytes. During mammalian regeneration, mononuclear-derived macrophages and self-renewing resident cardiac macrophages provide multiple cytokines and molecular signals that create a regenerative environment and cellular plasticity capacity in postnatal cardiomyocytes, a pivotal strategy for achieving myocardial repair. Consistent with other human tissues, cardiac macrophages originating from the embryonic endothelium produce a hierarchy of contributions to monocyte recruitment and fate specification. In this review, we discuss the novel functions of macrophages in triggering cardiac regeneration and repair after myocardial infarction and provide recent advances and prospective insights into the phenotypic transformation and heterogeneous features involving cardiac macrophages. In conclusion, macrophages contribute critically to regeneration, repair, and remodeling, and are challenging targets for cardiovascular therapeutic interventions.