SET-NUP214-induced hypermethylation landscape promotes abnormal overexpression of HOXC cluster genes in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia


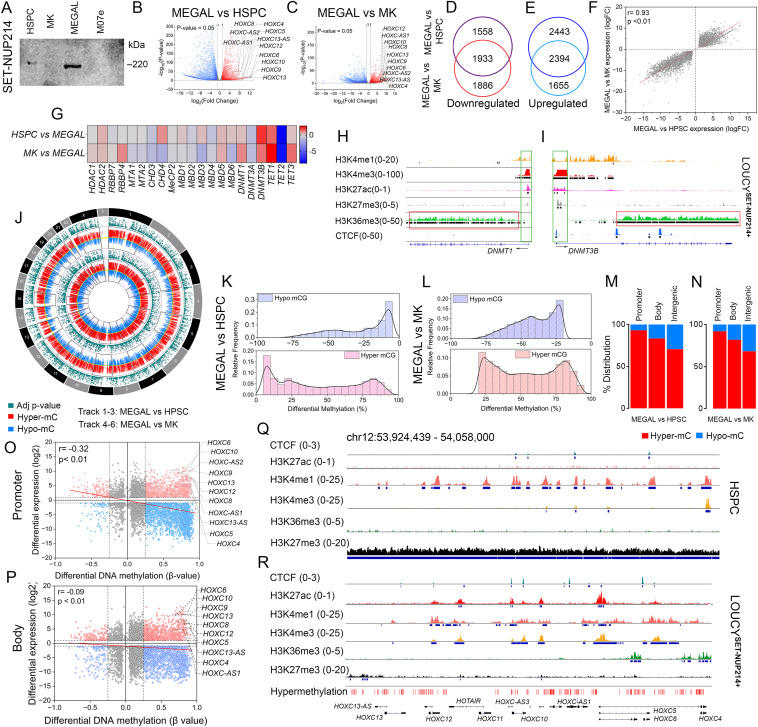
The SET-NUP214 gene fusion is mainly found in patients primarily diagnosed with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and rarely in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).1 Patients with the SET-NUP214 fusion protein (referred to as SN-214) have poor responses to allogeneic stem cell transplantation and a three-year disease-free survival rate of less than 40%.2 At the molecular level, the SN-214 fusion is known to recruit chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1) and disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L) proteins to the promoters of homeobox (HOX)-cluster genes, which is consistent with the overexpression of these genes in SN-214+ T-ALL.1 In contrast, silencing of the tumor suppressor gene, TET methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 (TET2), has been observed in the SN-214+ T-ALL cell line LOUCY due to hypermethylation at the promoter.3 However, the mechanism by which SN-214 alters the DNA methylation (DNAm) landscape to regulate leukemic transcriptional programs and signaling cascades, particularly in the myeloid lineage of leukemia, remains unexplored. Due to the rarity of the disease and the unavailability of genomic data from primary AML samples, our study focused on the MEGAL (ACC719, DSMZ) cell line. This cell line was identified as the only AML cell line expressing SN-214, and we used it to investigate the role of DNAm in leukemic transcriptional programs. To capture genome-wide DNAm and expression, we used the Infinium MethylationEPIC v2.0 BeadChip array and RNA sequencing, respectively. Considering the megakaryoblastic (M7, FAB classification) lineage of the MEGAL cell line, we analyzed the epigenetic changes in comparison to CD41+ megakaryocyte (MK) progenitors differentiated from umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ hematopoietic stem progenitor cells (HSPC). We also analyzed the chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing data from the LOUCY cell line to identify possible overlaps of the transcription factor CTCF and chromatin marks (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, H3K36me3, and H3K27me3) with differentially methylated CpGs (mC) in MEGAL. This integrative epigenetic analysis helped us understand the impact of the SN-214 fusion on leukemic transcriptional programs.