The important role and core marker gene of tumor-infiltrating plasma cells in the microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma


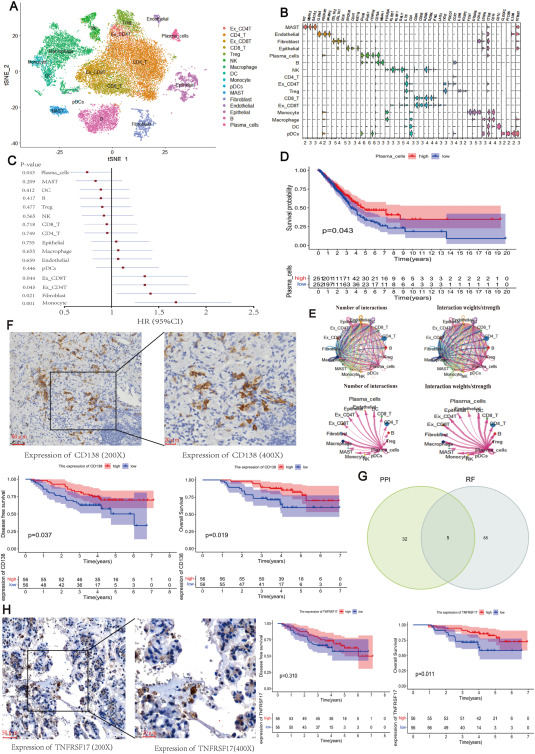
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the primary subtype of lung cancer, but its prognosis remains challenging. The tumor microenvironment plays a central role in the initiation and development of tumors, particularly regarding the composition of cell types. Understanding the cellular composition within tumors is crucial for comprehending disease processes and improving treatments. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) provides high-resolution gene expression data for single cells within tumors, allowing for precise analysis of different cell types and their gene expression profiles, but it lacks prognostic information. In contrast, bulk RNA sequencing (bulk RNA-seq) data contains plenty of prognostic information. Therefore, the deconvolution of scRNA-seq combined with bulk RNA-seq containing prognostic information is a favorable approach. In this study, we discovered a positive correlation between a high proportion of tumor-infiltrating plasma cells (PCs) and improved overall survival in LUAD. Through bioinformatics analysis, we identified TNFRSF17 as a potential key factor to improve prognosis in LUAD. This discovery was validated through immunohistochemical staining of clinical samples, suggesting that TNFRSF17 plays a pivotal role in the underlying mechanisms affecting LUAD prognosis.