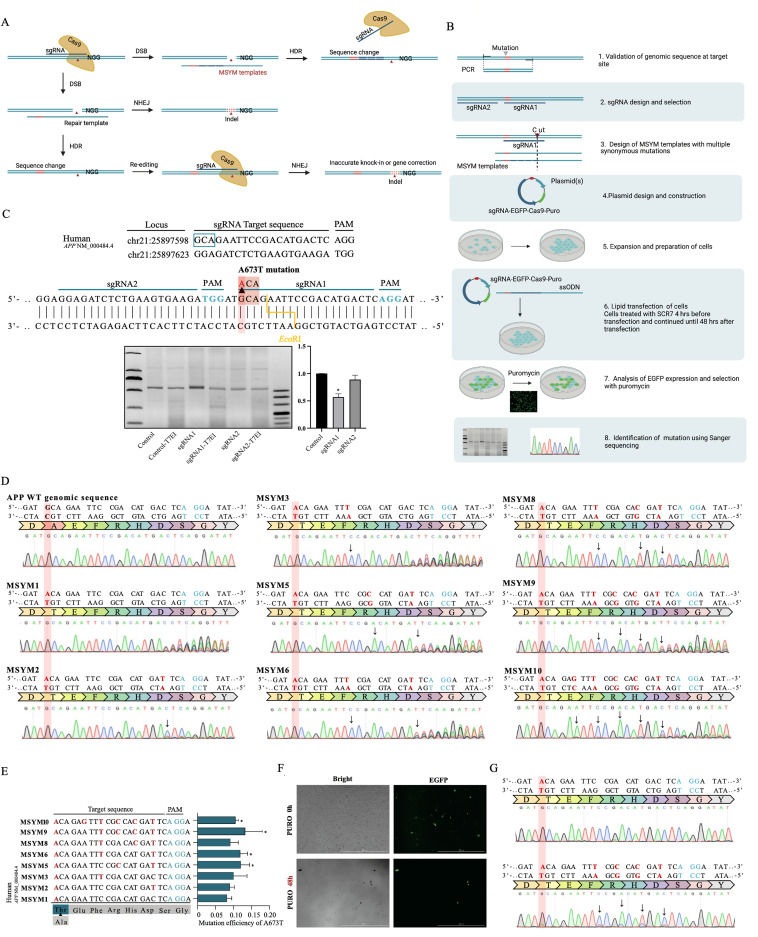
Precise and efficient insertion of A673T mutation in APP gene using MSYM


Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder causing memory loss, cognitive decline, language impairment, and disorientation, which impose an enormous burden on caregivers and the public health sector. A673T as a protective mutation has great therapeutic potential in AD.1,2 Therefore, a combination of stem cell therapy and A673T mutation existing in natural people based on gene targeting techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 have been suggested as promising and exciting new developments. Homology-directed repair (HDR), relatively rare in mammalian cells, is necessary to generate a specific sequence change such as point mutations.3 Efficient HDR and inefficient non-homologous DNA end joining are needed.4,5 Moreover, the HDR pathway repairs double-strand breaks via homologous recombination; a synthesized single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide (ssODN) with a homologous sequence as donor templates is simultaneously introduced, thereby enabling intended sequence changes.5 However, obstacles remain. HDR pathway disrupted by indels arises from subsequent re-editing in previously edited loci. The undesirable re-editing will recut the target loci until they are sufficiently modified to prevent further detection (Fig. 1A).