Alterations in expression and localization of POMGNT1 in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease


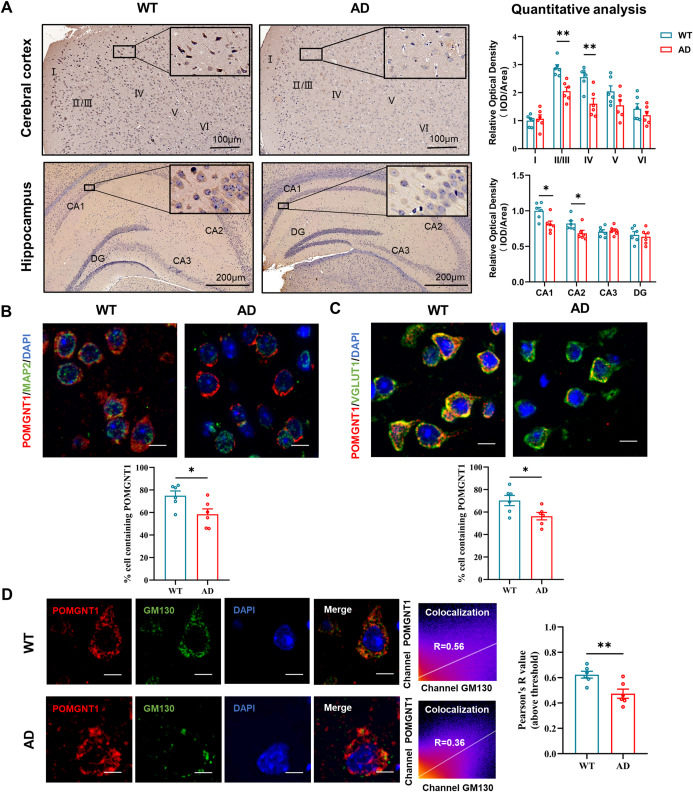
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex and progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes dementia in the aging population. One of the characteristic pathologic hallmarks of AD is the senile plaques, composed of the accumulation of β-amyloid. Neurotoxic β-amyloid results from the cleavage of transmembrane β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretases and γ-secretases, sequentially. O-mannosylation was found essential for the normal function of APP in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.1 Protein O-linked mannose β1,2-N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase 1 (POMGNT1) is a glycosyltransferase crucial for the elongation of O-mannosyl glycans and catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine from uridine 5′-diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine to O-mannose of glycoproteins.2 Robust evidence has implicated that aberrant expression or loss of POMGNT1 had an unfavorable effect on the central nervous system, such as cognition.3 Our previous study showed that overexpression of POMGNT1 inhibited amyloid production and hyperphosphorylation of Tau in the N2a/APP cell model of AD.4 These studies demonstrated that POMGNT1 may be a potential key molecule involved in the formation of amyloid peptides associated with the pathogenesis of AD. In this study, we aimed to reveal the altered localization of POMGNT1 in the brain of APP/PS1 mice compared with wild-type (WT) mice.