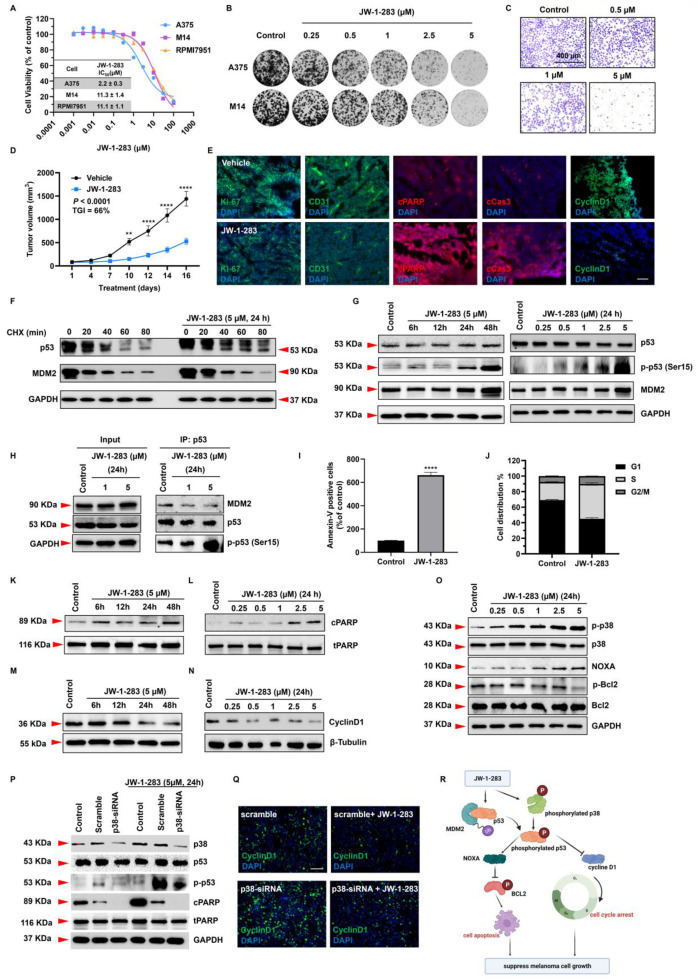
JW-1-283 inhibits melanoma tumor growth via stabilization of the p53 pathway


Melanoma is a lethal skin malignancy and the fifth most diagnosed cancer in the United States.1 Currently, for unresectable melanoma, the recommended treatment options include checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy targeting programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), and inhibitors targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway.2 However, the response rate may vary among the patients, and therefore demanding the development of novel treatment strategies. Tumor suppressor TP53 has been suggested as one of the critical regulators mediating the aggressiveness and progression of melanoma. Over 80% of melanoma patients harbor the wild type (WT) yet malfunctional p53, which leads to the investigation that focused on restoring the function of p53 in melanoma as an alternative treatment strategy.3 The degradation of p53 is catalyzed by mouse double minute 2 (MDM2), a well-known E3 ubiquitin ligase. Based on a previously reported MDM2 inhibitor, MX25, which has an iodide counter ion and is highly susceptible to oxidation in the air, we designed a new MX25 analog JW-1-283 using a stable ethyl sulfate group as the counter ion. In the current research, we investigated the anti-melanoma effect of JW-1-283 and leverages it as a novel p53-activating reagent.