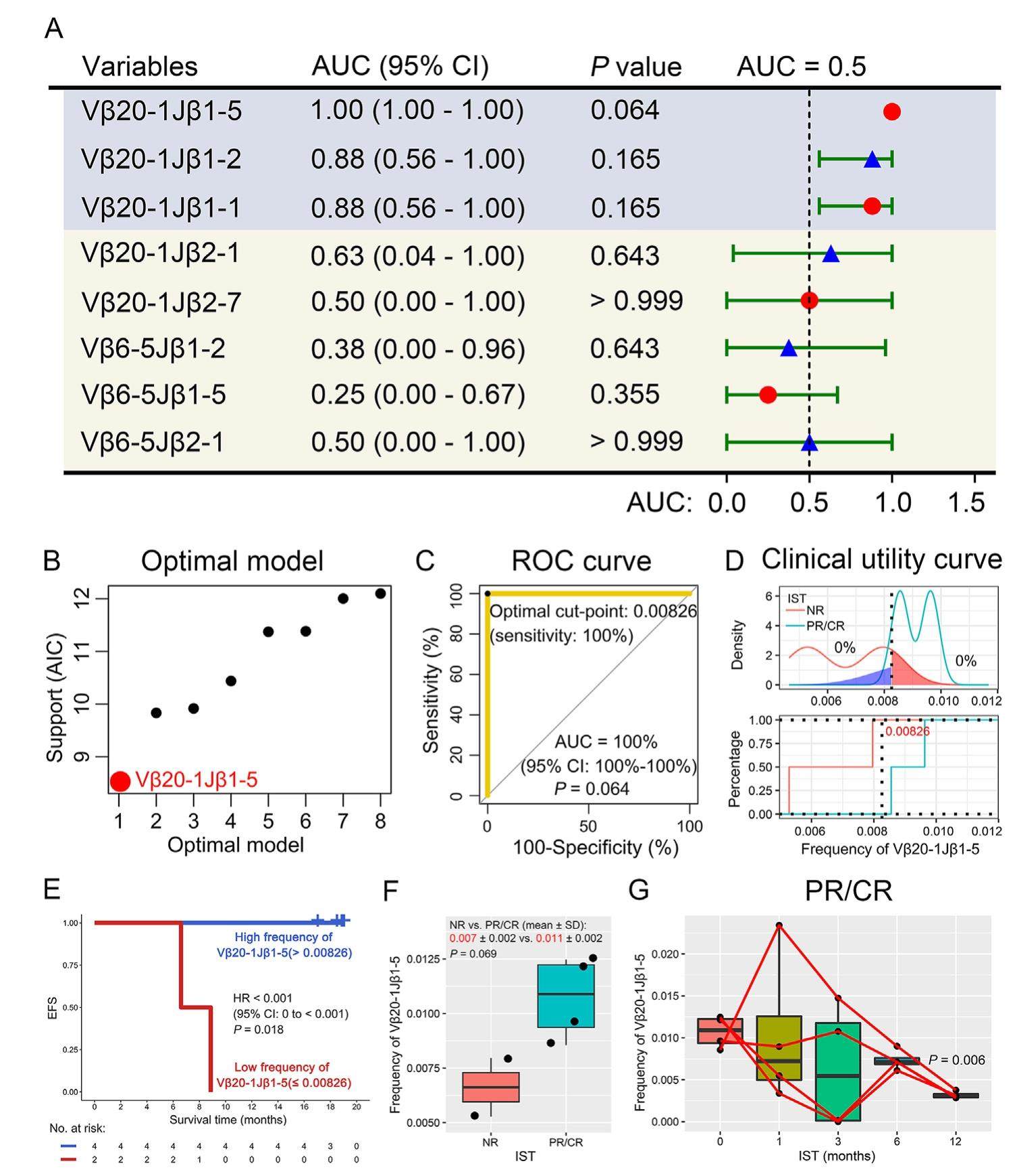
Predictive value of T cell receptor repertoire profiling for immunosuppressive therapy in severe aplastic anemia


Increasing evidence supports the hypothesis of autologous immune attack in severe aplastic anemia (SAA): the predominant role of activated cytotoxic T cells (CTL) expressing g-interferon in inhibiting the growth of bone marrow (BM) cells, putative autoantigens, and oligoclonal expansion of CD8+ T cells. For SAA patients, the definitive therapies are immunosuppressive therapy (IST) or hematopoietic stem transplantation (HSCT); IST is most widely applied in the clinic because of the lack of HLAmatched sibling or unrelated donors, patients’ age, and the cost of HSCT. However, only about 60% of SAA patients are responders after receiving IST, and less than 10% achieve complete remission (CR); effective biomarkers for the efficacy prediction of IST in SAA patients are lacking. Our previous publications have demonstrated that T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire profiling has been identified as a biomarker for predicting the clinical outcomes and efficacy of patients. However, systematic evaluation of the predictive value of the TCR repertoire for SAA patients during IST is still little known.