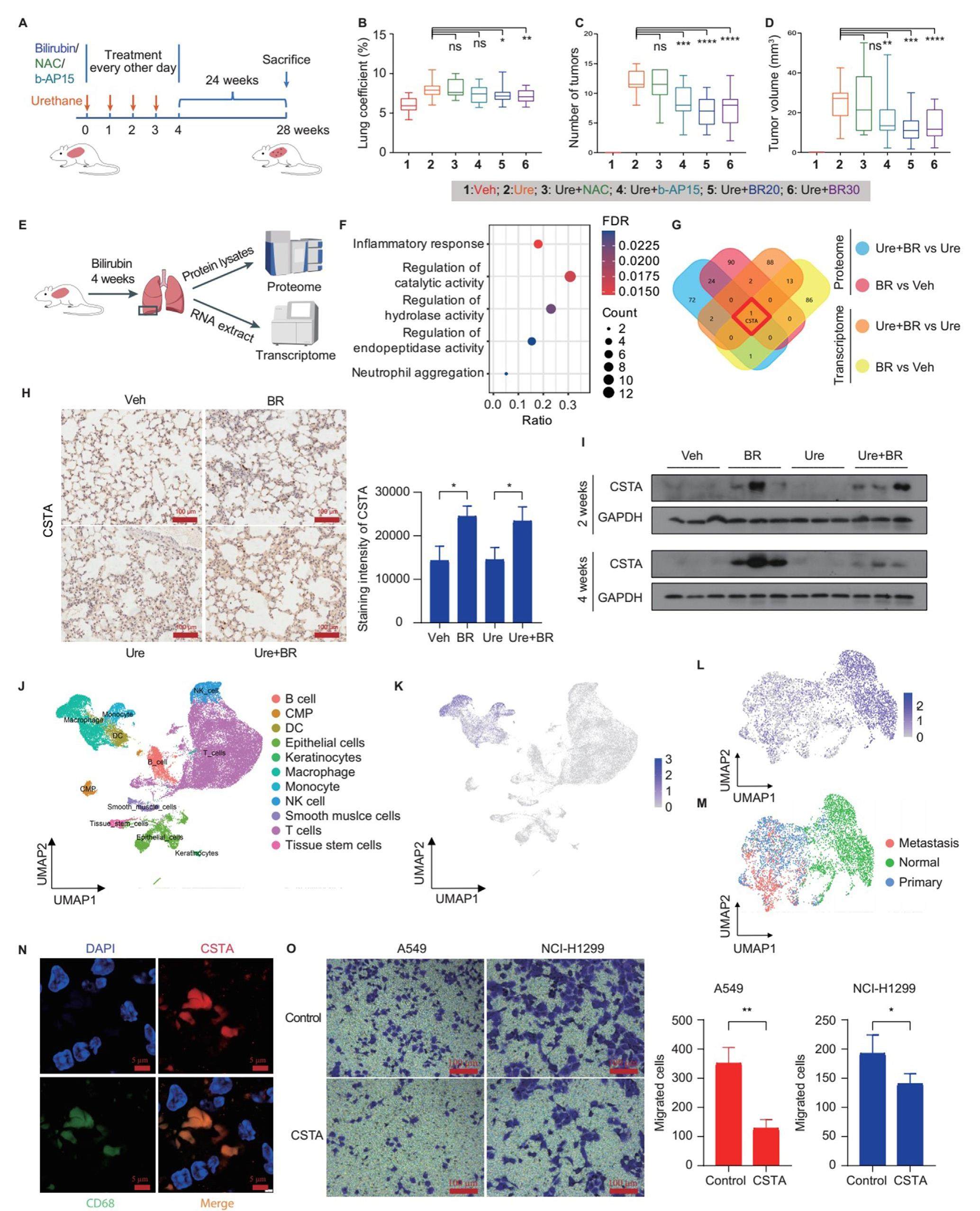
Bilirubin inhibits lung carcinogenesis by up-regulating cystatin A expression in tumor-infiltrating macrophages


As one of the leading causes of cancer deaths worldwide, the pathogenesis of lung cancer is still not completely understood. Bilirubin, a product of heme metabolism, has long been considered a waste product of the body. Increasing evidence suggests that bilirubin has additional antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and proteasome inhibitory activities. However, the specific role of bilirubin in the formation and development of lung cancer has not been elucidated.