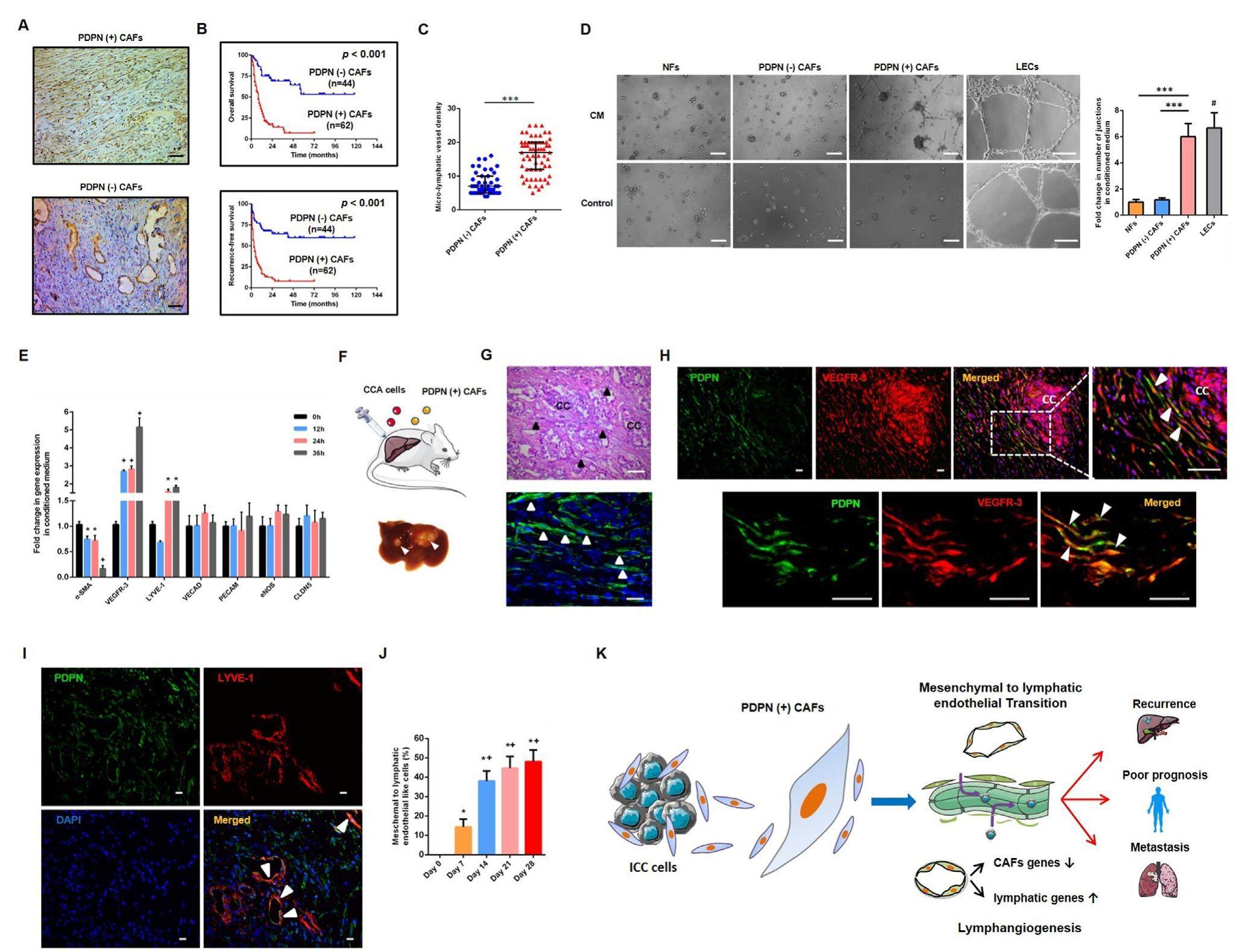
Novel discovery of PDPN-positive CAFs contributing to tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis through mesenchymal to lymphatic endothelial transition in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma


Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis is thought to be an important metastatic step in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), while the origin of tumor-associated lymphatic vessels within tumors is little known. Cancerassociated fibroblasts (CAFs) enhance tumor progression through many aspects. CAFs have been discovered exhibiting cellular plasticity of phenotypic transition - such as epithelialemesenchymal transition (EMT) - which promotes increased migratory and invasive capabilities of cells. However, mesenchymal-to-endothelial (MEndT) transition is yet to be identified in tumor entities. Podoplanin (PDPN), a 38-44 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein, is conventionally expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells. Recently, PDPN has also been discovered as a marker of CAFs, which is associated with cancer cell migration, invasion, and clinical prognosis. In several types of tumors such as breast cancer and lung adenocarcinoma, it was demonstrated that PDPN-expressing CAFs are correlated with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Based on abundant CAFs in ICC and PDPN expression in both CAFs and lymphatic endothelial cells, our study aims to investigate whether PDPN-positive CAFs could transform into lymphatic endothelial cells contributing to lymphangiogenesis in ICC.