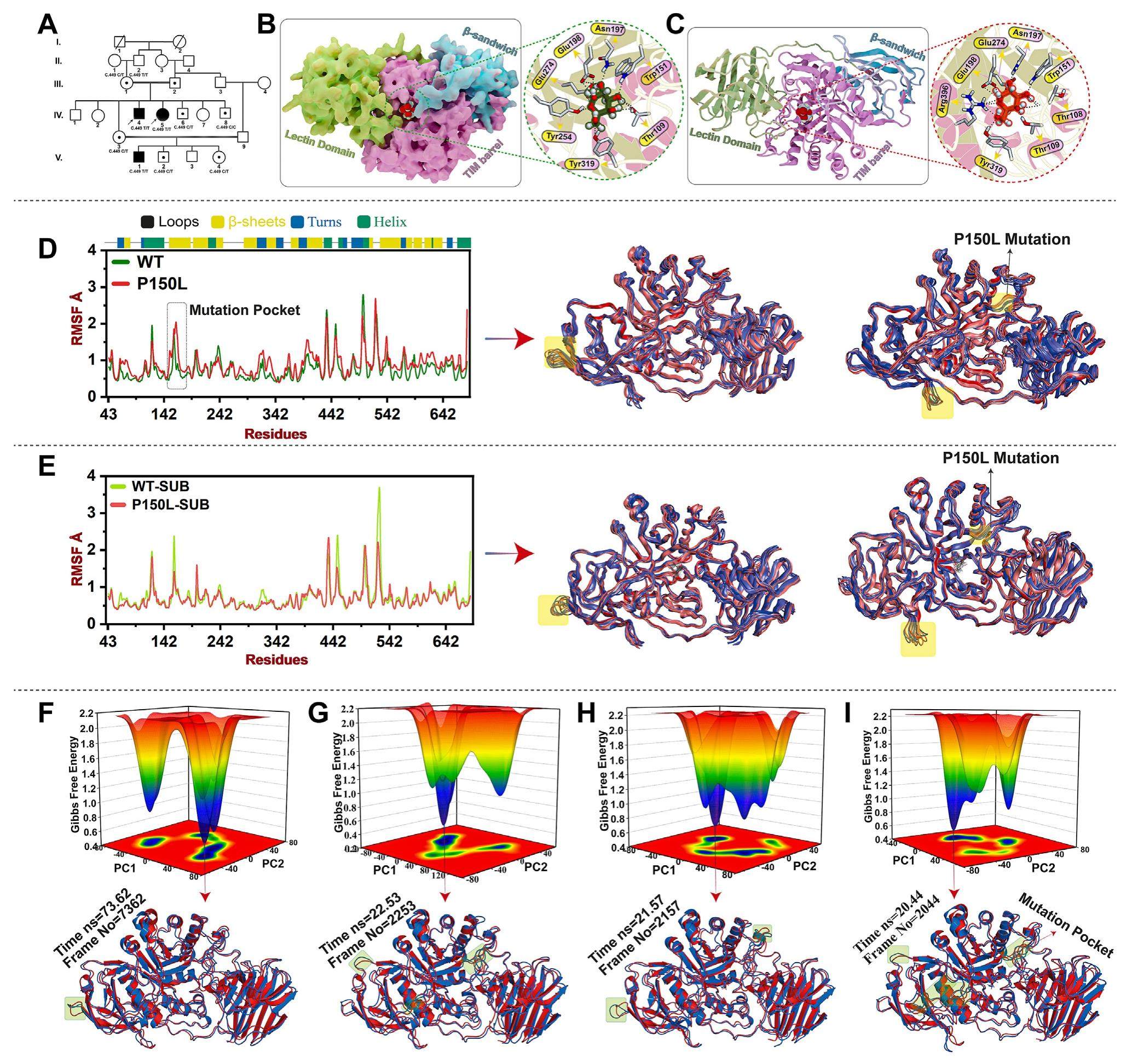
A novel variant of GALC in a familial case of Krabbe disease: Insights from structural bioinformatics and molecular dynamics simulation


Krabbe disease or globoid cell leukodystrophy (GLD; MIM#245200) is a rare and fatal lysosomal storage disease with an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance that results from the deficiency of galactocerebrosidase (GALC; E.C. 3.2.1.46), a lysosomal enzyme encoded by the GALC gene. GALC breaks down galactosylceramide, a cerebroside located mainly in the myelin sheath. Defects in GALC cause the accumulation of a cytotoxic metabolite, galactosylsphingosine or psychosine, which can be toxic to oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. The failure to digest galactosylceramide triggers the formation of multi-nucleated globoid cells, causing severe demyelination, axonopathy, and neuronal death. The reported frequency of Krabbe disease is 1 in 100,000 live births with symptoms including irritability, loss of motor ability, spasticity, ataxia, visual dysfunction, seizures, and cognitive impairment.