Transcriptomic landscapes underlying response and resistance to HDAC inhibitor chidamide in triple-negative breast cancer


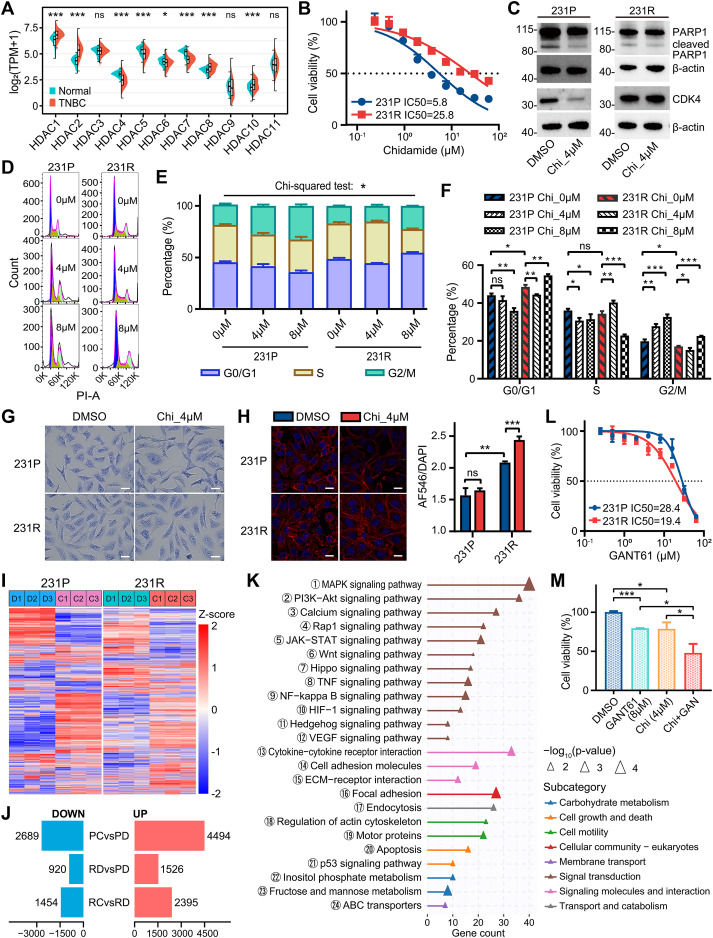
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains a medical challenge due to limited therapeutics.1 Histone deacetylases (HDACs) play vital roles in chromatin remodeling and epigenetics, and their dysregulation is implicated in malignancies, including TNBC.2 HDAC inhibitors (HDACis) have shown potent anti-TNBC activity in preclinical studies.3 Unfortunately, their clinical applications are beset by drug resistance, about which little is known.4 This study systematically explored the clinical significance of HDACs and transcriptomic landscapes underlying response and resistance to HDAC1/2/3/10 selective inhibitor chidamide,5 the first approved HDACi for solid tumor treatment, in TNBC.