Upregulated Krüppel-like factor 5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating Wnt3a signaling


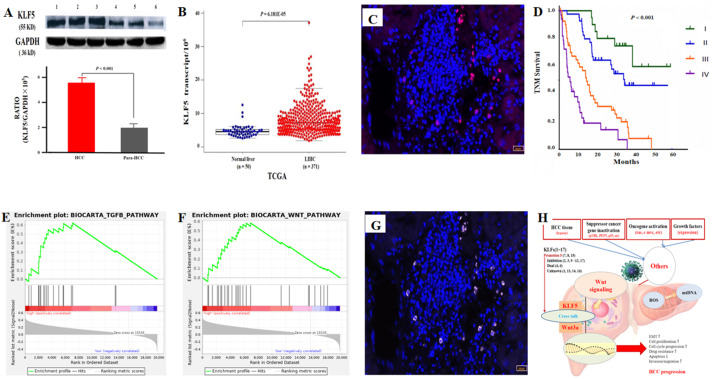
Early diagnosis and effective treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are crucial. Hepatocarcinogenesis involves multiple genes and processes with complicated mechanisms. Recently, zinc finger proteins (ZNFs) have been found to constitute the largest family in the human genome and are functional proteins involved in regulating cell differentiation, embryonic development, and a variety of diseases. Additionally, the regulation of target gene transcription factors can vary with environmental stimuli and cell type. Complex ZNFs with up to 13 Krüppel-like transcription factor (KLF) abnormalities are related to the progression of multiple types of tumors. Here, we report a new molecular marker, KLF5. The up-regulated KLF5 mRNAs in human HCC tissues were confirmed via The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, and abnormally increased KLF5 was analyzed in human HCC tissues via multicolor immunofluorescence technology. Additionally, the clinicopathological features of patients with KLF5 overexpression were TNM stage, tumor size, alpha fetoprotein (AFP) level, portal vein thrombosis, and HBV infection. High KLF5 expression was negatively correlated with the prognosis of HCC patients. Clinically, increased circulating KLF5 levels might be helpful in HCC diagnosis or differential diagnosis from patients with benign and malignant liver diseases. Mechanistically, KLF5 could be co-expressed with Wnt3a in the same HCC cells and might promote HCC progression via cross-talk.