Targeting STARD4/EGFR axis inhibits growth and overcomes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma


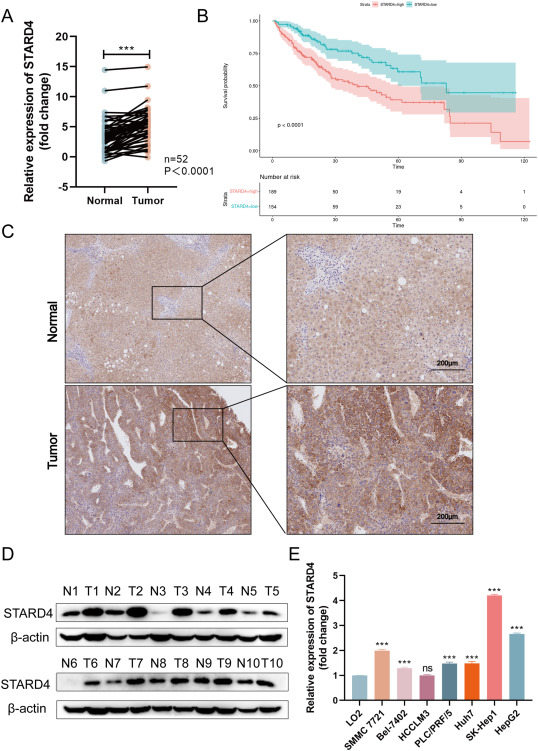
Lenvatinib is widely used as a first-line chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a highly metastatic and recurrent cancer. However, HCC cells often develop resistance to lenvatinib, thus reducing its efficacy. This study aims to investigate the impact of STARD4, a crucial cholesterol transporter, on HCC growth and lenvatinib resistance, as well as explore the involvement of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in STARD4's role. Analysis of clinical samples from HCC patients revealed increased expression of both STARD4 and EGFR in tumor tissues, with a strong correlation between STARD4 expression and malignancy progression. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that STARD4 promoted HCC growth and hindered lenvatinib's anti-tumor effect, while STARD4 down-regulation exerted opposite effects. Further investigation revealed that depletion of STARD4 increased cholesterol accumulation in the plasma membrane, resulting in reduced EGFR phosphorylation. Moreover, cholesterol depletion attenuated these effects, suggesting STARD4 activates EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling in a cholesterol-dependent manner. To elucidate the underlying mechanism of lenvatinib resistance, we established the lenvatinib-resistant HCC cell lines and found increased stimulation of both STARD4 and EGFR signaling. Furthermore, the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib suppressed the promotion of HCC progression by STARD4, reinforcing its role in activating the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that STARD4 enhances HCC growth and lenvatinib resistance by regulating cholesterol homeostasis and activating the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. These findings suggest STARD4 as a potential molecular biomarker for predicting lenvatinib resistance and as a therapeutic target in HCC treatment.